Unusual, photo-induced self-assembly of azobenzene-containing amphiphiles†
Abstract
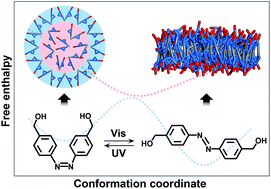
Stimuli-responsive self-assembly is playing an increasingly important role in emerging applications, ranging from smart materials to biosensors. However, obtaining essential information for further development, such as molecular arrangement and interaction, is still experimentally challenging. A molecular-level understanding of the stimuli-responsive self-assembly is needed. Azobenzene-containing (azo-containing) amphiphiles organize into photo-responsive assemblies because of the cis–trans isomerization triggered by the irradiation of ultraviolet (UV) and visible light. In this study, we applied a coarse grained (CG) molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, with the necessary potential parameters fitted from theoretical calculation data, to study the photo-induced self-assembly of 4,4′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-azobenzene (AzoCO), a simple azo-containing amphiphile. An unusual “chaotic micelle” and “monolayer phase” were obtained with cis- and trans-AzoCO molecules, respectively. The structural information and formation mechanism were studied. The “chaotic micelle” possesses a chaotic but not a pure hydrophobic interior as commonly understood. Through comparative simulations, we found that the azo (–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–) group of azobenzene plays a crucial role in the formation of the “chaotic micelle”. The “monolayer phase” is arranged by abreast rod-like trans-AzoCO molecules; the axial symmetry of the trans-AzoCO molecule drives the formation of this structure. The novel “chaotic micelle” and “monolayer phase” have potential applications in nanotechnology and bioengineering. This work is expected to trigger further studies on stimuli-responsive phenomena and materials.
N–) group of azobenzene plays a crucial role in the formation of the “chaotic micelle”. The “monolayer phase” is arranged by abreast rod-like trans-AzoCO molecules; the axial symmetry of the trans-AzoCO molecule drives the formation of this structure. The novel “chaotic micelle” and “monolayer phase” have potential applications in nanotechnology and bioengineering. This work is expected to trigger further studies on stimuli-responsive phenomena and materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...