Micro and macrorheology at fluid–fluid interfaces†
Abstract
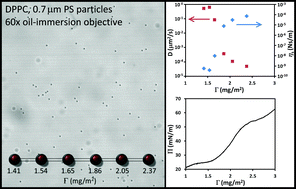
Interfacial transport phenomena play an important role in the dynamics of liquid interfaces found in emulsions, foams, and membranes. Both macroscopic and microscopic measurements of interfacial transport and rheology can be made, the former typically relying on the use of at least millimeter-scale probes, and the latter exploiting the motion of micrometer-scale probes. Recent publications have shown multiple orders of magnitude differences between experimentally observed diffusivities in passive microrheology, and the diffusivities expected based on macroscopic measurements of the surface rheology. In the present work, interfacial rheological measurements were made with both microrheological and macrorheological methods and the results are compared for different monolayers at an air–water interface. We have identified multiple aspects of particle-tracking microrheology that can contribute to orders-of-magnitude disagreement with macrorheological methods. In particular, unintentional tracking of particles not residing at the interface, the presence of large-scale interfacial heterogeneities, and underestimating static noise can all decrease estimates of surface viscosity from particle-tracking microrheology by orders of magnitude. After taking care to address these artifacts, we show that viscosities obtained from both methods agree well for poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) (PtBMA), and for dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), but disagree by orders of magnitude for hexadecanol. In poly(tert-butyl acrylate) (PtBA), large-scale heterogeneities prevented us from obtaining representative surface viscosities. By making surface viscosity measurements in an interfacial stress rheometer (ISR) with needles of different aspect ratio, we show that compressibility or Marangoni stress related effects may be contributing to the orders of magnitude disagreement in micro and macrorheological measurements observed in the hexadecanol system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...