Selective interactions of 5-(hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one with tetrabutylammonium fluoride and zinc(II) ions†
Prithiviraj Khakhlary and
Jubaraj B. Baruah*
Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati 781 039, Assam, India. Web: http://www.iitg.ernet.in/jubaE-mail: juba@iitg.ernet.in; Fax: +91-361-2690762; Tel: +91-361-2582311
First published on 20th November 2014
Abstract
5-(Hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one (HL) selectively interacts with tetrabutylammonium fluoride to form a supramolecular adduct. Formation of the supramolecular adduct in solution causes a drastic color change or causes quenching of the fluorescence emission of HL enabling its distinction from other tetrabutylammonium halides. Among different metal ions, addition of zinc ions to a solution of HL causes a selective color change or very distinguishable fluorescence emission intensity enhancement from other cations. The selective colouration of HL due to an increase in absorption at ∼640 nm in acidic condition in a similar way upon addition of zinc or fluoride ions is attributed to their ability to deprotonate HL. Di-aqua-bis(5-nitroso-8-oxyquinolinato)zinc(II) is structurally characterized. It shows strong visible absorption at 718 nm, which differs from the absorption of species formed in acidic conditions by zinc causing visual color change.
Introduction
Conventional fluoride sensors are based on two principles, namely guest displacement of a chromogenic receptor by fluoride ions or by specific reactions between chromogenic hosts with fluoride ions to cause color changes.1 Chelation induced optical properties of a metal complex can help to design receptors for fluoride ions.1c This leaves scope to develop simple chromogenic or fluorogenic metal complexes for detection and estimation of fluoride ions.1 Structurally simple oxy-quinolinate metal complexes are in use to detect fluoride ions.2 Uses of such complexes would reduce the complicacy involved in multi step syntheses of sensor molecules for fluoride ions.3 On the other hand, hydroxyquinoline derivatives form zinc complexes selectively; which have potential application in biology.4 Utility of zinc oxyquinolinate complexes has not been demonstrated for fluoride detection.5 With such a background, we explore the ability of 5-(hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one (HL) for selective anion and cation binding. Compound HL is chosen as it may adopt keto and enol form (Fig. 1); of which latter represents a hydroxyquinoline skeleton. On the other hand, oximes have ability to senses fluoride ions6 and fluoride ions can deprotonate hydroxy group.7 Hence these effects are anticipated to be operative with HL to cause changes in optical properties. Overall effect of ability of oximes to coordinate to zinc ions may be either cooperative or counterproductive in fluoride detection. To understand such facts, we studied interactions and optical properties changes on HL and its zinc complex on interaction with fluoride ions.Results and discussion
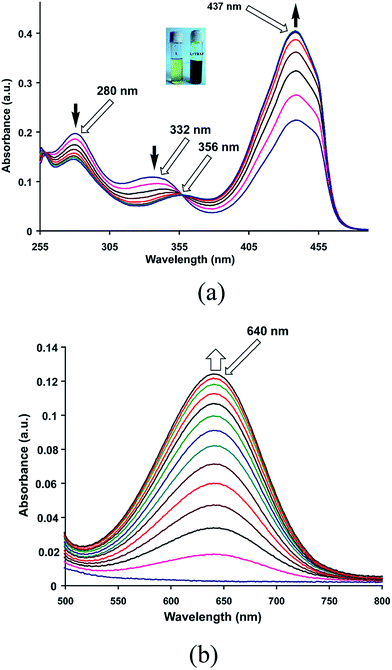
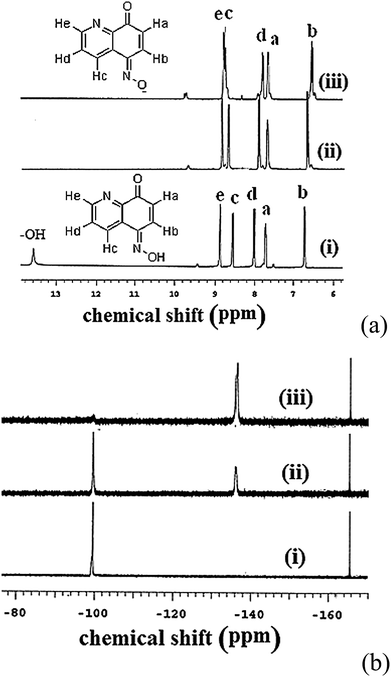
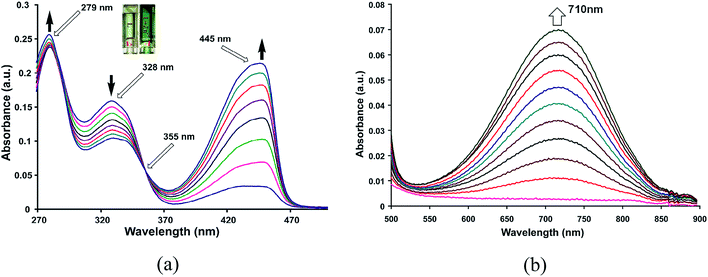
An intense green coloration of a solution of HL in dimethysulphoxide (DMSO) occurs on addition of tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF). This change is very specific to tetrabutylammonium fluoride and not caused by other tetrabutylammonium salts such as chloride, bromide, iodide, perchlorate, nitrate or bisulphate. Hence it enables selective visual detection of fluoride ions. Similar color change of a solution of HL in DMSO can also be brought about by other fluoride salts such as ammonium fluoride or sodium fluoride but not by other halides with similar cations. Color change is prominently reflected in increase in visible absorption at 437 nm of HL with a growth of a new absorption peak at 640 nm (Fig. 2a and b). From such changes fluoride ions can be detected in the range of 10−2 mol L−1 to 10−7 mol L−1 which is comparable to the detection limit of conventional fluoride ions sensors such as zirconium-oxyquinolate.8a,b Enhancement of intensity of absorption at 437 nm is associated with formation of an isobestic point at 356 nm, suggesting one to one transformation of HL to a colored species in solution. Acetate ions generally interfere in detection of fluoride ions,1d we also find a similar interference of ammonium acetate. Similarity in visible spectra of HL by acetate or fluoride ions, suggests a deprotonation of HL in solution by these ions. Color change of HL by fluoride ions are effectively visible by naked eyes at pH 4 or 7, however, compound HL turns dark green at pH 9, which disables detection of fluoride ions (ESI Fig. S1–S3†).This is reflected in the 1H-NMR spectroscopic titration of HL with TBAF. A comparison of signals appearing in 1H-NMR spectrum at aromatic region from solution of HL with or without TBAF is shown in Fig. 3a. Signals appearing in aliphatic region (1–3 ppm) from –CH2– and –CH3 groups of tetrabutylammonium cations remain invariant. 13C{1H}-NMR spectrum of HL shows a carbonyl peak at 183.4 ppm supports a keto form. 1H-NMR signal of OH at 13.4 ppm disappears on addition of TBAF, which suggests deprotonation of HL. The peak designated at Hc is in close proximity of the −ve charge of oximate, hence it is affected and chemical shift moves downfield.
A 1H-NMR titration was performed by adding triehylamine to a solution of HL in DMSO-d6; which also showed disappearance OH signal at 13.4 ppm (Fig. S4†). Since identical color change caused by fluoride ions to a solution of HL was also observed by adding triethylamine or a base to a solution of HL, hence interactions of these ions with HL is similar. In 19F-NMR TBAF showed a signal at −98.1 ppm, this signal disappeared on addition of HL and a new peak at −134.6 ppm appeared (Fig. 3b). On the other hand, reported 19F-NMR chemical shift for hydrofluoric acid in different solvents were different.11 Hence, the signal observed at −134.6 ppm is attributed to hydrogen fluoride formed in situ.
A solution of HL shows a fluorescence emission peak at 556 nm (λex = 475 nm). Fluoride ions cause quenching of this fluorescence emission of HL but other anions donot cause such quenching (Fig. S5–S9†). The fluorescence quenching is due to internal charge transfer between fluoride and the ligand, which is commonly caused by fluoride ions.1b Binding constant of fluoride ion with HL is calculated as 2.66 × 105 mol−1 L by Benesi–Hildebrand equation from absorption changes caused by TBAF.
A supramolecular 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
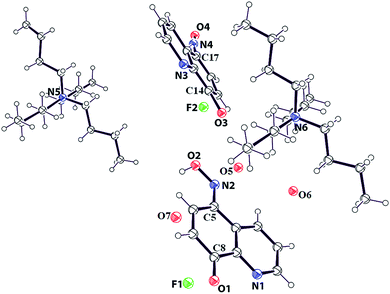
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 adduct of HL with TBAF in ratio, and having a water molecule as solvent of crystallization is structurally characterized (Fig. 4). Asymmetric unit of the supramolecular adduct has two molecules each of HL and TBAF which are symmetry independent. Both the symmetry independent HL molecules are in keto-forms. One of the HL is crystallographically disordered. The C8–O1 bond distance is 1.24 Å, it suggest it to be a C
1 adduct of HL with TBAF in ratio, and having a water molecule as solvent of crystallization is structurally characterized (Fig. 4). Asymmetric unit of the supramolecular adduct has two molecules each of HL and TBAF which are symmetry independent. Both the symmetry independent HL molecules are in keto-forms. One of the HL is crystallographically disordered. The C8–O1 bond distance is 1.24 Å, it suggest it to be a C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond, supporting a keto form. On the other hand, C5–N2 bond distance is 1.35 Å which is supportive of a conjugated C
O bond, supporting a keto form. On the other hand, C5–N2 bond distance is 1.35 Å which is supportive of a conjugated C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond. Comparing the structure with the reported structure of 5-(hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one9a and its salts9b it is found to be consistent with a keto-form.
N bond. Comparing the structure with the reported structure of 5-(hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one9a and its salts9b it is found to be consistent with a keto-form.
When zinc chloride was added to a solution of HL in methanol, intensity of absorptions at 445 nm increases (Fig. 5a) and a new visible absorption at 710 nm is observed (Fig. 5b). Other metal chloride salts such as Mn2+, Cd2+, Fe2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Al3+ etc. cause insignificant changes in visible spectra of HL (Fig. S10–S14†). Job's plot shows formation of a zinc complex with 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
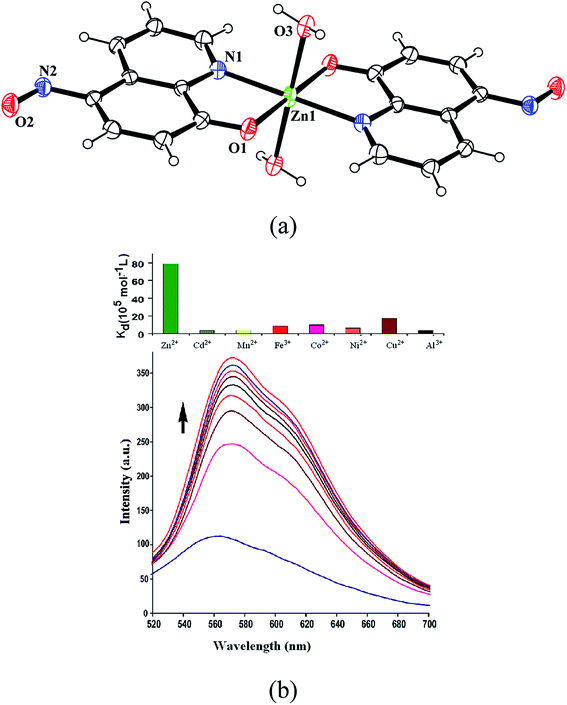
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 metal to ligand ratio (Fig. S15†). Complex formed in solution crystallizes as di-aqua-bis(5-nitroso-8-oxyquinolinato)zinc(II) is characterized by determining crystal structure (Fig. 6a). Complex has a distorted octahedral geometry with two apical positions occupied by two aqua ligands. Irrespective of metal to ligand ratio used in the reaction this zinc complex could be obtained, however this complex redissolved in DMSO solution dissociates giving double the number of peaks of parent ligand in 1H-NMR spectra. Observation of isobestic point in visible spectroscopic titration of zinc ions with HL showing increase in absorbance at 710 nm suggests this complex to be a contributing factor to color change. However, the absorbance observed at pH = 4 by addition of zinc chloride to a solution of HL shows absorption increase at ∼620 nm which is similar to the change caused by fluoride ions at this pH (Fig. S16†). But such an absorption is not observed at pH = 7. It may be mentioned that the acetate ions at pH = 4 causes very small change in coloration at 620 nm, hence these results indicate the fluoride and zinc to be special to deprotonate HL at mild acidic pH. It may be noted that the reaction of 8-hydroxyquinoline with zinc chloride is highly solvent dependent, it can result in tetranuclear cluster10 or it can result in complexes of [ZnCl4] along with zinc hydroxide.10b In the present case the solution of the zinc complex in DMSO shows nine NMR signals in aromatic region in contrast to the five signals of the parent compound (Fig. S17†). This supports instability on redissolution in DMSO. Ligand dissociation from the complex is confirmed by 1H-NMR titration of the complex by adding HL externally.
2 metal to ligand ratio (Fig. S15†). Complex formed in solution crystallizes as di-aqua-bis(5-nitroso-8-oxyquinolinato)zinc(II) is characterized by determining crystal structure (Fig. 6a). Complex has a distorted octahedral geometry with two apical positions occupied by two aqua ligands. Irrespective of metal to ligand ratio used in the reaction this zinc complex could be obtained, however this complex redissolved in DMSO solution dissociates giving double the number of peaks of parent ligand in 1H-NMR spectra. Observation of isobestic point in visible spectroscopic titration of zinc ions with HL showing increase in absorbance at 710 nm suggests this complex to be a contributing factor to color change. However, the absorbance observed at pH = 4 by addition of zinc chloride to a solution of HL shows absorption increase at ∼620 nm which is similar to the change caused by fluoride ions at this pH (Fig. S16†). But such an absorption is not observed at pH = 7. It may be mentioned that the acetate ions at pH = 4 causes very small change in coloration at 620 nm, hence these results indicate the fluoride and zinc to be special to deprotonate HL at mild acidic pH. It may be noted that the reaction of 8-hydroxyquinoline with zinc chloride is highly solvent dependent, it can result in tetranuclear cluster10 or it can result in complexes of [ZnCl4] along with zinc hydroxide.10b In the present case the solution of the zinc complex in DMSO shows nine NMR signals in aromatic region in contrast to the five signals of the parent compound (Fig. S17†). This supports instability on redissolution in DMSO. Ligand dissociation from the complex is confirmed by 1H-NMR titration of the complex by adding HL externally.
Di-aqua-bis(5-nitroso-8-oxyquinolinato)zinc(II) complex reacts with TBAF, which changes its visible absorption by shifting it from 718 nm to 676 nm through an isobestic point at 660 nm (Fig. S18†). This happens due to replacement of L by fluoride ions. Addition of zinc(II) chloride to a solution of HL in presence of TBAF shifts absorption peak at 640 nm to 710 nm (Fig. S19†) and absorption at 710 nm of a solution of HL with zinc chloride (Fig. S20†) increases on addition of TBAF. Thus the zinc complex can be constructed or dislodged by adequate concentration of fluoride and HL. Other tetrabutylammonium salt such as chloride, bromide, perchlorate or nitrate does not change visible spectra of the complex at these pHs.
Chelation induced changes of fluorescence emission of HL is observed in presence of various metal ions. Fluorescence titrations of HL with zinc(II) [Fig. 6b (bottom)], cadmium(II) or aluminium(iii) chloride in methanol show increase in fluorescence emission intensity (Fig. S21 and S22†). Whereas, addition of metal chloride of paramagnetic ions such as Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+ or Cu2+ quench fluorescence emission. Metal ions such as Na+, K+, Be2+, Mg2+, Ca2+ or In3+ shows insignificant changes in emission spectra of HL (Fig. S23–S27†). Binding constants of HL with metal ions are in order of Zn2+ ≫ Cu2+ > Co2+ > Fe2+ > Ni2+ > Mn2+ > Cd2+ > Al3+. Relative binding constants are illustrated in a bar diagram shown on top of Fig. 6b. Zinc ions have highest binding constant 78.7 × 105 mol−1 L relative to other metal ions. Among the quenchers, Cu2+ ions are most effective and have a binding constant 17.45 × 105 mol−1 L. Paramagnetic Cu2+ ions generally causes quenching of fluorescence.12 On the other hand, zinc ions have higher binding ability to HL than binding ability of HL with fluoride ions. Despite of this fact fluoride ions replace HL from zinc complex, this is attributed to higher electro-negativity of fluoride.
In conclusions supramolecular adduct of 5-(hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one with fluoride ion and a mononuclear complex of zinc are isolated and characterized. Fluoride ions could be visually distinguished from numbers of anions at slightly acidic pH. Fluoride as well as acetate ions quench fluorescence emission of HL which distinguishes them from other common neutral anions. Several cations can enhance intensity of fluorescence emission of HL independently but zinc ions are special to show sharp enhancement of fluorescence intensity. Several metal ions bring about quenching of fluorescence which enables zinc ions to be distinguished from other cations. Similarity between fluoride ions and zinc ions in showing color change in acidic condition makes HL an unique example.
Experimental
Infrared spectra (KBr pellets) of solid samples were recorded in the region 4000–400 cm−1 on a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum-One FT-IR spectrophotometer. UV-visible spectra were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer-Lambda 750 UV-visible spectrometer at room temperature. Mass spectra were recorded on a micro mass Q-TOF (waters) mass spectrometer by using an acetonitrile/formic acid matrix. Fluorescence emission spectra were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer LS-55 spectrofluorimeter by taking definite amount of each sample and exciting at required wavelength.5-(Hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one was prepared by slightly modifying reported procedure13 provided in ESI.†
Synthesis of di-aqua-bis(5-nitroso-8-oxyquinolinato)zinc(II)
To a solution of 5-(hydroxyimino)quinolin-8-one (0.348 g, 1 mmol) in methanol, anhydrous zinc chloride (0.137 g, 1 mmol) was added and stirred for half an hour. A green precipitate obtained was filtered and redissloved in dimethylformamide. Solution on standing for one week resulted dark green crystals of the zinc complex. Isolated yield: 95%. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3204 (w), 1605 (s), 1577 (m), 1549 (s), 1529 (s), 1493 (m), 1444 (w), 1411 (w), 1375 (w), 1357 (w), 1305 (m), 1277 (s), 1244 (s), 1148 (s), 1106 (w), 1065 (w), 1027 (w), 819 (w), 796 (w), 741 (w), 692 (w), 502 (w), 473 (w). Elemental analysis calcd for C18H14N4O6Zn, C, 48.25%; H, 3.15%; N, 12.51%; found C, 48.21%, H, 3.33%, N, 12.86%. Crystallographic parameters: crystal system, triclinic; space group, P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) ; temperature, 296(2) K; wavelength, 0.71073 Å; a, 7.2755(9) Å; b, 7.9392(9) Å; c, 8.4103(9) Å; α, 64.840(11)°; β, 74.394(10)°; γ, 87.012(10)°; V, 422.41(8) Å3; Z = 1, density, 1.760 g cm−3; abs. coeff., 1.503 mm−1; abs. correction, multi-scan; F(000), 228; total nos of reflections, 1533; reflections I > 2σ(I), 1297; max. 2θ, 50.50°; ranges (h, k, l) −8 ≤ h ≤ 8, −8 ≤ k ≤ 9, −8 ≤ l ≤ 10; completeness to 2θ, 99.8%; refinement method, full-matrix least-squares on F2; data/restraints/parameters, 2304/0/199; Goof (F2), 0.924; R indices [I > 2σ(I)], 0.0417; R indices (all data), 0.0539.
; temperature, 296(2) K; wavelength, 0.71073 Å; a, 7.2755(9) Å; b, 7.9392(9) Å; c, 8.4103(9) Å; α, 64.840(11)°; β, 74.394(10)°; γ, 87.012(10)°; V, 422.41(8) Å3; Z = 1, density, 1.760 g cm−3; abs. coeff., 1.503 mm−1; abs. correction, multi-scan; F(000), 228; total nos of reflections, 1533; reflections I > 2σ(I), 1297; max. 2θ, 50.50°; ranges (h, k, l) −8 ≤ h ≤ 8, −8 ≤ k ≤ 9, −8 ≤ l ≤ 10; completeness to 2θ, 99.8%; refinement method, full-matrix least-squares on F2; data/restraints/parameters, 2304/0/199; Goof (F2), 0.924; R indices [I > 2σ(I)], 0.0417; R indices (all data), 0.0539.
Supramolecular adduct of TBAF with HL was prepared by slow evaporation of a solution of TBAF and HL in 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 molar ratio in dimethylsulphoxide. Few blue crystals could be obtained after 3 weeks. 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, ppm): 8.78 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.82 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (d, J = 10.4 Hz, 1H), 3.16 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 8H), 1.56 (m, 8H), 1.31 (m, 8H), 0.92 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 12H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, ppm): 182.7, 149.7, 146.8, 143.6, 131.6, 130.2, 127.5, 126.22, 122.9, 57.5, 23.1, 19.2, 13.4. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3442 (w), 1603 (s), 1573 (m), 1529 (s), 1488 (m), 1466 (w), 1380 (w), 1303 (w), 1129 (m), 1277 (s), 1105 (w), 1065 (w), 796 (w), 737 (w). Elemental anal calcd for C9H6N2O2·C16H36NF·H2O, C, 66.19; H, 9.78; N, 9.26; found C, 65.98; H. 9.76; N, 9.12%. Formula, C50H82F2N6O7; mol. wt 917.22; crystal system, monoclinic; space group, P21/c; temperature, 296(2) K; wavelength, 0.71073 Å; a, 22.5699(14) Å; b, 9.4519(7) Å; c, 26.9700(17) Å; α, 90.00°; β, 104.307(3)°; γ, 90.00°; V, 5575.0(6) Å3; Z = 4, density, 1.093 g cm−3; abs. coeff., 0.077 mm−1; abs. correction, multi-scan; F(000), 1992; total nos of reflections, 9788; reflections I > 2σ(I), 5798; max. 2θ, 50.00°; ranges (h, k, l) −26 ≤ h ≤ 26, −11 ≤ k ≤ 11, −32 ≤ l ≤ 32; completeness to 2θ, 99.8%; refinement method, full-matrix least-squares on F2; data/restraints/parameters, 9788/18/583; Goof (F2), 1.351; R indices [I > 2σ(I)], 0.0988; R indices (all data), 0.2106.
1 molar ratio in dimethylsulphoxide. Few blue crystals could be obtained after 3 weeks. 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, ppm): 8.78 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.82 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (d, J = 10.4 Hz, 1H), 3.16 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 8H), 1.56 (m, 8H), 1.31 (m, 8H), 0.92 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 12H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, ppm): 182.7, 149.7, 146.8, 143.6, 131.6, 130.2, 127.5, 126.22, 122.9, 57.5, 23.1, 19.2, 13.4. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3442 (w), 1603 (s), 1573 (m), 1529 (s), 1488 (m), 1466 (w), 1380 (w), 1303 (w), 1129 (m), 1277 (s), 1105 (w), 1065 (w), 796 (w), 737 (w). Elemental anal calcd for C9H6N2O2·C16H36NF·H2O, C, 66.19; H, 9.78; N, 9.26; found C, 65.98; H. 9.76; N, 9.12%. Formula, C50H82F2N6O7; mol. wt 917.22; crystal system, monoclinic; space group, P21/c; temperature, 296(2) K; wavelength, 0.71073 Å; a, 22.5699(14) Å; b, 9.4519(7) Å; c, 26.9700(17) Å; α, 90.00°; β, 104.307(3)°; γ, 90.00°; V, 5575.0(6) Å3; Z = 4, density, 1.093 g cm−3; abs. coeff., 0.077 mm−1; abs. correction, multi-scan; F(000), 1992; total nos of reflections, 9788; reflections I > 2σ(I), 5798; max. 2θ, 50.00°; ranges (h, k, l) −26 ≤ h ≤ 26, −11 ≤ k ≤ 11, −32 ≤ l ≤ 32; completeness to 2θ, 99.8%; refinement method, full-matrix least-squares on F2; data/restraints/parameters, 9788/18/583; Goof (F2), 1.351; R indices [I > 2σ(I)], 0.0988; R indices (all data), 0.2106.
Measurement of absorption or emission: respective solution of tetrabutylammonium salt or of metal chloride was prepared in methanol or DMSO. These solutions were independently titrated with solution of HL (3 mL, 10−5 mol L−1) taken in quartz cuvette. Titrations were done by adding desired amount of solution of salts with the aid of a microliter syringe in aliquots and recording the UV-visible or fluorescence emission spectra after each addition.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New-Delhi India for financial support.References
- (a) F. Hinterholzinger, B. Ruhle, S. Wuttke, K. Karaghiosoff and T. Bein, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 2562 CrossRef PubMed; (b) C. Caltagirone and P. A. Gale, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 520–563 RSC; (c) S. Y. Kim and J. I. Hong, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 3109–3112 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) C. Suksai and T. Tuntulani, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2003, 32, 192–202 RSC; (e) M. Cametti and K. Rissanen, Chem. Commun., 2009, 2809–2828 RSC; (f) R. Hu, J. Feng, D. Hu, S. Wang, S. Li, Y. Li and G. Yang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 4915–4918 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) R. S. Sujith, G. N. Rao and C. Janadhana, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2006, 65, 565–570 CrossRef PubMed; (b) T. Balaji and H. Matsunaga, Anal. Sci., 2005, 2, 973–977 CrossRef; (c) P. Jones, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1992, 258, 123–127 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. M. Bayon, A. R. Garcia, J. I. G. Alonso and A. Saz-Medel, Analyst, 1999, 124, 27–31 RSC.
- (a) K. Kanagaraj and K. Pitchumani, Chem.–Asian J., 2014, 9, 146–152 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Lenormand, J.-P. Goddard and L. Fensterbank, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 748–751 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) B. Garg, T. B. Bhist and S. M. S. Chauhan, New J. Chem., 2010, 34, 1251–1254 RSC; (d) S. H. Mashraqui, R. Betkar, M. Chandiramani, D. Quinonero and A. Frontera, Tetrahedron Lett., 2010, 51, 596–599 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. Kumar, V. Luxami and A. Kumar, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 5549–5552 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) Y. Qu, J. Hua and H. Tian, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 3320–3323 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) Q. S. Lu, L. Dong, J. Zhang, J. Li, L. Jiang, Y. Huang, S. Qin, C.-W. Hu and X.-Q. Yu, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 669–672 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) V. Bhalla, H. Singh and M. Kumar, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 628–631 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) X. Peng, Y. Wu, J. Fan, M. Tian and K. Han, J. Org. Chem., 2005, 70, 10524–10531 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) S. V. Bhosale, M. B. Kalyankar and S. J. Langford, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 4858–4861 CrossRef PubMed; (k) P. Sokkalingam and C.-H. Lee, J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76, 3820–3828 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) P. Bose and P. Ghosh, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 2962–2964 RSC; (m) P. Bose, B. N. Ahamed and P. Ghosh, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 1972–1979 RSC; (n) Y. Shiraishi, H. Maehara and T. Hirai, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2009, 7, 2072–2076 RSC; (o) J. K. Day, C. Bresner, N. D. Coombs, I. A. Fallis, L. L. Ooi and S. Aldridge, Inorg. Chem., 2008, 47, 793–804 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (p) T. W. Hudnall and F. P. Gabbai, Chem. Commun., 2008, 4596–4597 RSC; (q) R. M. Duke and T. Gunnlaugsson, Tetrahedron Lett., 2007, 48, 8043–8047 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (r) C. H. Zhao, E. Sakuda, A. Wakamiya and S. Yamaguchi, Chem.–Eur. J., 2009, 15, 10603–10612 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (s) R. M. F. Batista, E. Oliveira, S. P. G. Costa, C. Lodeiro and M. M. M. Raposo, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 3201–3204 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (t) T. Neumann, Y. Dienes and T. Baumgartner, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 495–497 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (u) M. A. Hossain, J. M. Llinares, S. Mason, P. Morehouse, D. Powell and K. Bowman-James, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 2335–2338 CrossRef.
- D. A. Pearce, N. Jotterand, I. S. Carrico and B. Imperiali, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 5160–5161 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. E. McQuade and S. J. Lippard, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 9535–9545 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. Tomat and S. J. Lippard, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2010, 14, 225–230 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Rouffet, C. Augusto, F. DeOliveira, Y. Udi, A. Agarwal, I. Sagi, J. A. McCammon and S. M. Cohen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 8232–8233 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) C. J. Fahrni and T. V. O'Halloran, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 11448–11458 CrossRef CAS; (e) Y. Zhang, X. F. Guo, W. X. Si, L. H. Jia and X. H. Qian, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 473–476 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) X. Y. Chen, J. Shi, Y. M. Li, F. L. Wang, X. Wu, Q. X. Guo and L. Liu, Org. Lett., 2009, 1, 4426–4429 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) N. Okabe and M. Akita, Acta crystallographica Section C, Crystal Structure Communications, 1997, 53, 1324–1325 Search PubMed; (b) P. Khakhlary and J. B. Baruah, J. Chem. Sci., 2015 Search PubMed , in press.
- (a) Q. Wang, Y. Xie, Y. Ding, X. Li and W. Zhu, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 3669–3671 RSC; (b) P. E. Jackson, Trends Anal. Chem., 2001, 20, 320–329 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. Dutzler, E. B. Campbell, M. Cadene, B. T. Chait and R. MacKinnon, Nature, 2002, 415, 287–294 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Devaraj, D. Saravanakumar and M. Kandaswamy, Tetrahedron Lett., 2007, 48, 3077–3081 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) V. Luxami and S. Kumar, Tetrahedron Lett., 2007, 48, 3083–3087 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) D. A. Jose, P. Kar, D. Koly, B. Ganguly, W. Thiel, H. N. Ghosh and A. Das, Inorg. Chem., 2007, 46, 5576–5584 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) V. Amendola and L. Fabbrizzi, Chem. Commun., 2009, 513–531 RSC.
- (a) C. B. Rosen, D. J. Hansen and K. V. Gothelf, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 7916–7922 RSC; (b) J. H. Clark, Can. J. Chem., 1979, 57, 1481–1487 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) B. Taner, O. Alici and P. Deveci, Supramol. Chem., 2014, 26, 119–124 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. Wang, Q. Wang, Y. Sun, Y. Wang, G. Zhao and Y. Cui, J. Serb. Chem. Soc., 2011, 76, 529 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. Khakhlary and J. B. Baruah, J. Chem. Sci., 2015 Search PubMed , in press.
- K. O. Christe and W. W. Wilson, J. Fluorine Chem., 1990, 46, 339–342 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Gouanve, T. Schuster, E. Allard, R. Meallet-Renault and C. Larpent, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2007, 17, 2746–2756 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) T. Ishikawa, T. Watanabe, H. Tanigawa, T. Saito, K.-I. Kotake and H. Ohashi, J. Org. Chem., 1996, 61, 2774–2779 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. A. Isaev, I. I. Lomovskii, K. G. Korolev and R. K. Karimov, Chem. Heterocycl. Compd., 2005, 41, 1027–1030 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Synthetic procedure of HL, 1H-NMR titration of HL with zinc salt, various fluorescence and visible spectroscopic titrations are available. CCDC 1024294 and 983710. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c4ra13805h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |