Water soluble well-defined acidic graft copolymers based on a poly(propylene glycol) macromonomer
Abstract
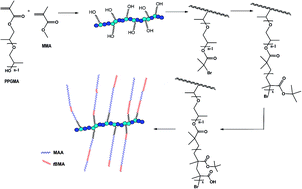
A series of well-defined amphiphilic graft copolymers based on poly(propylene glycol)methacrylate (PPGMA) extended with a polymethacrylate segment containing methacrylic acid units was successfully synthesized, combining atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), esterification, “grafting from” polymerization, and acidolysis. The multistep procedure yielded hydroxy-functionalized polymers (6–47 mol% of PPGMA), bromoester-functionalized copolymers as multifunctional macroinitiators (nBr = 8–25), PPGMA-based copolymers with poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) (PtBMA) segments (DPtBMA = 18–59), and copolymers varying in hydrophilic fraction content (FMAA = 0.28–0.54). After the generation of methacrylic acid units the PPGMA-based graft polymers attained a good solubility in polar solvents such as methanol and water. The particles, which were formed in aqueous solution, achieved sizes in the nanoscale range (165–230 nm) and negative zeta potentials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...