Synergistic protective effect of chlorogenic acid, apigenin and caffeic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in male mice
Abstract
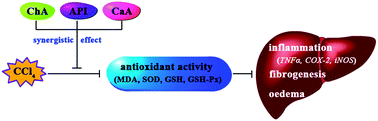
Polyphenol compounds widely exist in plant-derived foods, such as coffee beans, fruits, vegetables, olive oils and wines. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that chlorogenic acid (ChA), apigenin (API) and caffeic acid (CaA) possess various pharmacological effects, such as antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the synergistic protective effects of them on tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury remains unclear. To explore these effects, male mice were administrated CCl4 together with or without pretreatment of ChA, API, CaA or their co-treatments for 30 days. The serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased in CCl4-treated mice (P < 0.001), and these effects were further confirmed by liver histopathological observation. In addition, CCl4 could increase the hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) formation; decrease the level of hepatic reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (P < 0.001). ChA, API and CaA significantly attenuated CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity, especially when they were co-administrated. The factorial analysis indicated that ChA + API + CaA has the strongest synergistic protective effect on CCl4-induced reduction of antioxidative activity (P ≤ 0.001). As compared with the CCl4-treated group, the mRNA expression of inflammatory mediators, including tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were significantly downregulated by co-treatment with ChA, API or CaA (P < 0.05). And they also had a synergistic protective effect on CCl4-induced up-regulation of the inflammation mediators (P < 0.01). Our study for the first time revealed the synergistic protective effect of ChA, API and CaA on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...