Synthesis of γ-nitroaldehydes containing quaternary carbon in the α-position using a 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase whole-cell biocatalyst†
Abstract
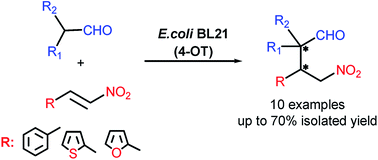
Synthesis of γ-nitroaldehydes from branched chain aldehydes and a range of α,β-unsaturated nitroalkenes was achieved by a whole-cell biocatalytic reaction using 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase as catalyst. Under mild conditions, cyclic and acyclic branched aldehydes were converted into synthetically valuable quaternary carbon containing γ-nitroaldehydes. The yields of the desired products were influenced by reaction condition parameters such as organic solvent, temperature and pH. The whole-cell biocatalytic approach to the generation of α,α-substituted γ-nitroaldehydes was compared to the organocatalytic approach involving the lithium salt of phenylalanine as a catalyst. As the resulting γ-nitroaldehydes exhibited moderate antifungal activity and mild in vitro cytotoxicity against human fibroblasts (0.2–0.4 mM) they could further be examined as potentially useful pharmaceutical synthons.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...