Isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone: effect of substituents and concentration on anion sensing selectivity and sensitivity†
Marek Cigáň*,
Klaudia Jakusová,
Jana Donovalová,
Vojtech Szöcs and
Anton Gáplovský
Faculty of Natural Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Comenius University, Mlynská dolina CH-2, SK-842 15 Bratislava, Slovakia. E-mail: cigan@fns.uniba.sk
First published on 17th October 2014
Abstract
The effect of substituent and concentration on anion sensing selectivity and sensitivity of nine new easily synthesized isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone E-isomer sensors IIIa–XIa was investigated. The substantial difference between the association constants for IIIa–XIa interaction with strongly and weakly basic anions allows detection of F− or CH3COO− anions even at high weakly basic anion excess. Substitution in position 5- of the isatin ring and para-substitution on the phenyl ring in the phenylsemicarbazide chain influence sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion complex stoichiometry and thus also sensor sensitivity. Detection limits of 3–4 × 10−7 mol dm−3 for F− and CH3COO− anions by sensors IVa and Va bearing electron-withdrawing substituents are among the lowest published detection limits for these anions in organic solvents. The high selectivity and sensitivity of sensor VIa allows confident F− detection at tolerated fluoride drinking-water level. The solution dilution leads to a dramatic change in sensor selectivity. Consequently, one E-isomer can be used to sense both strongly and weakly basic anions. On the other side, higher sensor solution concentrations increase the F− and CH3COO− anion detection range, similar to the additional Z-isomer utilization.
anion complex stoichiometry and thus also sensor sensitivity. Detection limits of 3–4 × 10−7 mol dm−3 for F− and CH3COO− anions by sensors IVa and Va bearing electron-withdrawing substituents are among the lowest published detection limits for these anions in organic solvents. The high selectivity and sensitivity of sensor VIa allows confident F− detection at tolerated fluoride drinking-water level. The solution dilution leads to a dramatic change in sensor selectivity. Consequently, one E-isomer can be used to sense both strongly and weakly basic anions. On the other side, higher sensor solution concentrations increase the F− and CH3COO− anion detection range, similar to the additional Z-isomer utilization.
Introduction
Ion and neutral molecule recognition and signalling are currently amongst the most intense emerging areas of supramolecular chemistry. While anions play a very important role in many chemical and biological processes, their identification and quantification are quite complex; especially in biological systems. One way to overcome this problem is to utilize new optical receptors specifically designed for individual anions. Supramolecular chemistry has focused on the development of selective colorimetric or fluorescent anion sensors for the last twenty years,1–4 and researches including Wenzel, Chudzinski, Bergamaschi, Jiménez, Martínez-Máñez and Gale continue this work.5–10Anions and receptors interact together particularly through hydrogen bonding interactions.4,11–14 Due to the facile synthesis and easily-tunable NH acidity, amides, ureas and thioureas persist as the most widely employed hydrogen bond donor groups in anion receptor systems.10
Anion induced tautomerism and the light and thermally initiated mutual E- and Z-isomer transformations of two efficient and easily synthesized isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone colorimetric sensors were investigated in our recent three studies (ESI, Scheme S1†).15–17 Therein, the interaction of F−, AcO−, H2PO4−, Br− and HSO4− anions with E- and Z-isomers of isatin-3-4-phenyl(semicarbazone) I and N-methylisatin-3-4-phenyl(semicarbazone) II as sensors influenced the equilibrium ratio of the individual sensor tautomeric forms in the liquid phase.
The E- and Z-sensor isomers differed in sensitivity, selectivity and sensing mechanism. UV-VIS spectroscopy readily determined the equilibrium ratio of the individual tautomeric forms affected by; (1) the inter- and intra-molecular interaction modulation of isatinphenylsemicarbazone molecules by anion induced changes in receptor molecule solvation shells and (2) the sensor–anion interaction with urea hydrogens. Appropriate selection of experimental conditions resulted in a high degree of sensor selectivity for some investigated anions. Sensors Ia–IIb provided both excellent signal to noise ratio and wide detection range. Detection of F− or CH3COO− anions at high weakly-basic anion excess was also possible. Furthermore, due to excellent E isomer sensitivity in organic media, these isomers can be used for F− or CH3COO− sensing in semi-aqueous media. The photodegradation of E-isomer anion sensors Ia and IIa due to light initiated E–Z isomerization may complicate the anion detection, therefore care should be taken when interpreting data for quantitative determination of anions using Ia and IIa E-isomers. However, photochemical E–Z isomerization efficiency is relatively low at ΦE–Z < 0.01, and this allows reliable detection of strongly basic anions using Ia or IIa. In addition, the easy E-isomer transformation to the corresponding Z-isomer and the utilization of both isomers significantly increases the detection range for F− and CH3COO− anions valid for Ia or IIa in organic media from 10−6 to 10−4 mol dm−3 to 10−6 to 10−2 mol dm−3 of F− or CH3COO−. Although zero efficiency of back photochemical Z–E isomerization excludes the use of isatinphenylsemicarbazones I and II as molecular switches, the absence of thermally initiated E–Z isomerization and both photochemically and thermally initiated back Z–E isomerizations in strongly interacting polar solvents are beneficial for Ia and IIa E-isomer application in chemical actinometry.
Strongly basic anions influence the solvation shell of the E-isomer self-associate, and this interaction leads to formation of the non-associated hydrazide. Concurrently, strongly basic anions interact mostly with the highly acidic NH hydrogen of hydrazide resulting in hydrazonol formation. This is sharply contrasted with most urea and thiourea based sensors which interact with CH3COO− in double hydrogen bonding to the Y-shaped urea/thiourea moiety.9,18,19 The reason for this anomalous isatin N-phenylsemicarbazones behaviour is the lower energy of its s-cis, s-trans –NHCONH– structural fragment conformation compared to the Y-shaped s-trans, s-trans –NHCONH– arrangement.17
Herein, the substituent and dilution effect on anion sensing of nine new isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone E-isomers IIIa–XIa is reported (Scheme 1); including the determination of light initiated E–Z isomerization quantum yield (ΦE–Z). The properties of these nine sensors with various substituents in position 5- of the isatin or in the phenyl ring para-position are compared with those for the unsubstituted Ia E-isomer. This research is necessary for practical application of these compounds as anion sensors and also for development and design of new effective anion sensors. In addition, concepts of sensing selectivity, sensitivity, detection range and detection limit for these colorimetric sensors, together with mathematical analysis of the well-known relation for association constants Kass determination, are discussed in this paper.
Results and discussion
Sensor selectivity
Anion presence affects the degree of IIIa–XIa self-association in the DMF solution.16 In the presence of strongly basic anions (F− and CH3COO−), the IIIa–XIa E-isomers transform from their self-associate hydrazide A (keto) form to hydrazonolate (enolate) form B (Scheme 2). | ||
| Scheme 2 Presumed interaction of derivatives Ia and IIIa–XIa with F− (or CH3COO−) anions during Ia solution titration with TBA+F− (or TBA+CH3COO−). | ||
This transformation is accompanied by a decrease in absorption intensity at approximately 330 nm and increased absorption at approximately 410 nm (Fig. 1 and ESI, Fig. S1 and S2†).
Similar to the result observed for Ia, the addition of weakly basic anions such as Br− and HSO4− shifts the tautomeric hydrazide/hydrazonol equilibrium for all substituted IIIa–XIa derivatives to the hydrazide form A. Absortion band intensity at approximately 410 nm decreases in the presence of these anions in contrast to the F− and CH3COO− effect (ESI, Fig. S3 and S4†).
Because the anion–receptor 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 Kass constants higher than 105 cannot be determined precisely by UV-VIS spectroscopy (see Appendix A), sensor selectivity was investigated in DMF
1 Kass constants higher than 105 cannot be determined precisely by UV-VIS spectroscopy (see Appendix A), sensor selectivity was investigated in DMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O (9
H2O (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; v/v) solvent mixture (Table 1 and ESI, Fig. S5 and S6†). However, the large Kass sensitivity to additional anion–receptor interactions in the high anion concentration region does not allow correct selectivity comparison for IIIa–XIa sensors from their Kass values alone (see Appendix B).
1; v/v) solvent mixture (Table 1 and ESI, Fig. S5 and S6†). However, the large Kass sensitivity to additional anion–receptor interactions in the high anion concentration region does not allow correct selectivity comparison for IIIa–XIa sensors from their Kass values alone (see Appendix B).
| Association constants – Kass | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compd | Anion | |||
| F− | R2 | CH3COO− | R2 | |
a Sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 2 anion 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex – Kass in mol−2 dm6; cE-isomer = 1 × 10−4 mol−1 dm3; R2 – coefficient of determination (average value). 1 complex – Kass in mol−2 dm6; cE-isomer = 1 × 10−4 mol−1 dm3; R2 – coefficient of determination (average value). |
||||
| Ia | (6.7 ± 0.2) × 103 | 0.9963 | (1.6 ± 0.5) × 104 | 0.9673 |
| IIIa | (5.2 ± 0.2) × 103 | 0.9906 | (7.7 ± 0.2) × 103 | 0.9934 |
| IVa | (1.2 ± 0.1) × 104 | 0.9810 | (1.2 ± 0.1) × 104 | 0.9864 |
| Va | (2.9 ± 0.7) × 104 | 0.9421 | (2.2 ± 0.3) × 104 | 0.9710 |
| VIa | (5.6 ± 1.8) × 104 | 0.9869 | (8.6 ± 4.1) × 106a | 0.9581 |
| VIIa | (5.3 ± 0.1) × 103 | 0.9784 | (9.0 ± 0.6) × 103 | 0.9898 |
| VIIIa | (5.4 ± 0.8) × 103 | 0.9853 | (1.2 ± 0.0) × 104 | 0.9874 |
| IXa | (5.1 ± 0.6) × 104 | 0.9942 | (4.8 ± 2.3) × 107a | 0.9728 |
| Xa | (5.7 ± 3.2) × 107a | 0.9663 | (1.7 ± 0.9) × 108a | 0.9574 |
| XIa | (2.4 ± 0.1) × 103 | 0.9967 | (1.3 ± 0.1) × 104 | 0.9697 |
Interestingly, the –CN, –Br and –OCF3 electron-withdrawing substituents in VIa, IXa and Xa change the sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion binding stoichiometry to 2
anion binding stoichiometry to 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and thus further complicates IIIa–XIa Kass comparison. In these cases, one anion binds two sensor molecules (Table 1 and ESI, Fig. S7†).
1 and thus further complicates IIIa–XIa Kass comparison. In these cases, one anion binds two sensor molecules (Table 1 and ESI, Fig. S7†).
Despite the above mentioned complexities encountered in Kass determination for 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 IIIa–XIa complexes with strongly basic anions, the Kass values higher than 1 × 104 for IIIa–XIa
1 IIIa–XIa complexes with strongly basic anions, the Kass values higher than 1 × 104 for IIIa–XIa![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) F− and IIIa–XIa
F− and IIIa–XIa![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CH3COO− 1
CH3COO− 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes and the Kass above 1 × 107 for sensor
1 complexes and the Kass above 1 × 107 for sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 2
anion 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes indicate exceptionally strong F− and CH3COO− anion binding. Therefore, strongly basic anion addition leads rather to the NH group deprotonation than to the hydrazide/hydrazonol tautomeric equilibrium shift resulting in sensor
1 complexes indicate exceptionally strong F− and CH3COO− anion binding. Therefore, strongly basic anion addition leads rather to the NH group deprotonation than to the hydrazide/hydrazonol tautomeric equilibrium shift resulting in sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) hydrazonol 1
hydrazonol 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex formation bounded by one hydrogen bond (as we assumed in our previous article).16 Absorbance increase at 410 nm during titration process in non-polar CHCl3, where the hydrazonol is not formed, supports this conclusion.
1 complex formation bounded by one hydrogen bond (as we assumed in our previous article).16 Absorbance increase at 410 nm during titration process in non-polar CHCl3, where the hydrazonol is not formed, supports this conclusion.
In the case of sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 2
anion 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes, one aggregate (dimer) molecule is transformed to hydrazonolate B and the second hydrazide molecule is stabilized by the solvent as hydrazonol form. The tendency to form 2
1 complexes, one aggregate (dimer) molecule is transformed to hydrazonolate B and the second hydrazide molecule is stabilized by the solvent as hydrazonol form. The tendency to form 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes therefore correlates fairly well with the hydrazonol form stabilization by solvation that increases in isatin N-phenylsemicarbazones with electron-withdrawing substituents (ESI, Fig. S8 and S9†).
1 complexes therefore correlates fairly well with the hydrazonol form stabilization by solvation that increases in isatin N-phenylsemicarbazones with electron-withdrawing substituents (ESI, Fig. S8 and S9†).
Substantial difference between the Kass values for IIIa–XIa interaction with strongly and weakly basic anions allows detection of F− and CH3COO− anions even at high weakly basic anion excess (Kass = 101 to 102 for Br− or HSO4− anions).
Sensor sensitivity
Sensitivity denotes sensor ability to detect an analyte at a specified concentration. Sensor sensitivity depends not only on sensor–anion interaction strength (Kass) but also on sensor signal changes following anion-binding.The sensitivity of isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone IIIa–XIa E-isomers was compared by introducing the Γ sensitivity parameter which describes detection-wavelength absorbance changes in the presence of 1 equivalent of anion.
Substitution in position 5- of the isatin ring and para-substitution in the phenylsemicarbazide chain phenyl ring influence Γ value (Fig. 2 and ESI, Fig. S10†). Although mainly electron-withdrawing substituents increase the Γ sensor sensitivity value, Γ increase correlates rather with the sensor ability to form 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes than with the increasing strength of electron-withdrawing group. However, the absence of sensitivity increase in Xa forming the most stable 2
1 complexes than with the increasing strength of electron-withdrawing group. However, the absence of sensitivity increase in Xa forming the most stable 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex (Table 1) and the sensitivity order change in DMF compared to DMF
1 complex (Table 1) and the sensitivity order change in DMF compared to DMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O solvent mixture point out the complexity of sensor/sensor, sensor/anion and sensor/solvent interactions (Fig. 2 and ESI, Fig. S10†). Combination of these processes creates the complexity of resultant substituent influence on sensor sensitivity.
H2O solvent mixture point out the complexity of sensor/sensor, sensor/anion and sensor/solvent interactions (Fig. 2 and ESI, Fig. S10†). Combination of these processes creates the complexity of resultant substituent influence on sensor sensitivity.
The IIIa–XIa E-isomer sensitivity for weakly basic Br− and HSO4− anions at 10−5 mol dm−3 sensor concentration in solution is almost 1000-times lower than for F− and CH3COO− anions.
Detection limit (3σ/S) is the lowest concentration level determined statistically different from a blank with 99% confidence and quantification limit (10σ/S) is the level above which quantitative results are obtained with a specified degree of confidence. The calculated detection and quantification limits for F−, CH3COO−, Br− and HSO4− anions using the most important isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone E-isomer sensors from the Ia–XIa set are summarized in Table 2. The determined 3σ/S for strongly basic F− and CH3COO− anions by sensors IVa and Va are amongst the lowest published detection limits for these anions in organic solvent.20–23 At 10−5 mol dm−3 sensor concentration, the tautomeric hydrazide–hydrazonol equilibrium is completely shifted to the hydrazonol side, and isatin N-phenylsemicarbazones can be used as sensors for weakly basic anions. Sensor solution dilution thus leads to dramatic change in sensor selectivity. Therefore, the one E-isomer can be used for both strongly and weakly basic anion detection. The determined 3σ/S for Br− and HSO4− anions in DMF for some isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone sensors is highlighted in Table 2. Their values are in the 0.2–0.4 mmol dm−3 range.
| Compd | 3σ/S [μM] | 10σ/S [μM] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anion | ||||||||
| F−b | CH3COO−b | Br−c | HSO4−c | F−b | CH3COO−b | Br−c | HSO4−c | |
| a μM = μmol dm−3 = 10−6 mol dm−3.b cE-isomer = 1 × 10−4 mol−1 dm3.c cE-isomer = 1 × 10−5 mol−1 dm3. | ||||||||
| Ia | 0.7 | — | — | — | 2.3 | — | — | — |
| IVa | 0.4 | 0.3 | 280 | 200 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 930 | 680 |
| Va | 0.3 | 1.0 | 290 | — | 1.1 | 3.5 | 960 | — |
| VIa | 1.0 | 0.6 | — | — | 3.2 | 2.0 | — | — |
| VIIa | 0.5 | 0.9 | — | — | 1.6 | 3.0 | — | — |
| IXa | — | 1.3 | — | — | — | 4.5 | — | — |
| Xa | — | — | 320 | 280 | — | — | 1100 | 930 |
| XIa | — | — | 220 | — | — | — | 720 | — |
Detection range
Detection range is an important factor in anion sensing. The utilization of Z-isomers with lower sensitivity can significantly increase the F− or CH3COO− anion detection range valid for IIIa–XIa in organic media from approximately 0.005–1 equivalent to 0.005–100 equivalent of isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone (from 5 × 10−7 to 10−4 mol dm−3 to 5 × 10−7 to 10−2 mol dm−3 of F− and CH3COO−) (Fig. 3 and S11†). The photochemical E–Z isomerization efficiency for IIIa–XIa is relatively low at ΦE–Z < 0.01. This is similar to the situation in the unsubstituted Ia E-isomer and it allows IIIa–XIa reliable detection of strong basic anions (ESI, Table S1†).Furthermore, the ΦE–Z values for substituted IIIa–XIa E-isomers at 10−4 mol dm−3 concentration are approximately 2-fold lower than for the unsubstituted Ia E-isomer. ΦE–Z decrease following electron-withdrawing substitution in position 5- of the isatin ring and also in para-position on the phenyl ring is connected with the enhanced tendency towards hydrazonol formation (ESI, Fig. S8 and S9†).15 Unexpected ΦE–Z decrease following also electron-donating substitution is probably linked to the enhanced aggregate variability. Neither excitation nor solution heating Z-isomers led to back conversion to the corresponding E-isomers; similar to the situation in the unsubstituted Ia Z-isomer.
Sensor concentration increase and simultaneous optical path length decrease also increase E-isomer sensors IIIa–XIa anion detection range (Fig. 4). Although increased IVa concentration decreases sensor sensitivity, it allows acetate anion detection range increase from 3 × 10−7 to 5 × 10−5 mol dm−3 to 3 × 10−7 to 1 × 10−3 mol dm−3 CH3COO−.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 CH3COO− anion detection range increase using E-isomer sensor IVa accomplished by sensor concentration increase and simultaneous decrease in optical path length. | ||
Anion detection in aqueous media
Detection of anions in aqueous environments is currently one of the most interesting target in the chemosensor field.19 However, this is unachievable for most designs relying on hydrogen bonding, since even minute amounts of water disrupt these interactions. Moreover, sensor molecules are often such complex constructs that several synthetic steps are required for their preparation.10,20E-Isomers IIIa–XIa are synthesized in a one step facile condensation of isatine with the corresponding phenylsemicarbazide in high reaction yield. Due to excellent IIIa–XIa E-isomer sensitivity in organic media, these isomers can also be used for F− or CH3COO− sensing in semi-aqueous media (Fig. 5).
The determined low detection limit 3σ/S = 1.3 × 10−6 mol dm−3 (10σ/S = 4.3 × 10−6 mol dm−3) for F− anions in 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 DMF
1 DMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O mixture by sensor VIa allows the confident F− detection at the tolerated fluoride level of 1.5 mg L−1 (0.17 mmol dm−3) in drinking water. On the other side, E-isomer IXa with low 3σ/S = 1.4 × 10−6 mol dm−3 for CH3COO− in 9
H2O mixture by sensor VIa allows the confident F− detection at the tolerated fluoride level of 1.5 mg L−1 (0.17 mmol dm−3) in drinking water. On the other side, E-isomer IXa with low 3σ/S = 1.4 × 10−6 mol dm−3 for CH3COO− in 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 DMF
1 DMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O mixture can be a useful sensor for CH3COO− determination in biological samples with low F− concentration. However, because the addition of strongly basic OH− anions has the same effect as F− or CH3COO− anion addition, care must be taken when interpreting data in semi-aqueous media from aqueous samples at pH above 10.16 In addition, the CO2(g)/HCO3−/CO32− equilibrium may also play an important role.
H2O mixture can be a useful sensor for CH3COO− determination in biological samples with low F− concentration. However, because the addition of strongly basic OH− anions has the same effect as F− or CH3COO− anion addition, care must be taken when interpreting data in semi-aqueous media from aqueous samples at pH above 10.16 In addition, the CO2(g)/HCO3−/CO32− equilibrium may also play an important role.
Conclusion
This paper investigated the effect of substituent and concentration on anion sensing selectivity and sensitivity of nine new easily synthesized isatin N-phenylsemicarbazone E-isomer sensors IIIa–XIa.Although the large Kass sensitivity to additional anion–receptor interactions in the high anion concentration region does not allow correct selectivity comparison for IIIa–XIa sensors from their Kass values, it can be concluded that the Kass values higher than 1 × 104 in DMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O (9
H2O (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; v/v) solvent mixture and Kass higher than 1 × 107 for 2
1; v/v) solvent mixture and Kass higher than 1 × 107 for 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 anion–sensor interactions indicate exceptionally strong F− and CH3COO− anion binding. Addition of strongly basic anion leads to the NH group deprotonation and not to the sensor
1 anion–sensor interactions indicate exceptionally strong F− and CH3COO− anion binding. Addition of strongly basic anion leads to the NH group deprotonation and not to the sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) hydrazonol 1
hydrazonol 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex formation that we assumed in our previous article. In the case of sensor
1 complex formation that we assumed in our previous article. In the case of sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 2
anion 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes, one aggregate (dimer) molecule is deprotonated to hydrazonolate B and the second hydrazide molecule is stabilized by solvation as the hydrazonol form. The tendency to form 2
1 complexes, one aggregate (dimer) molecule is deprotonated to hydrazonolate B and the second hydrazide molecule is stabilized by solvation as the hydrazonol form. The tendency to form 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes correlates fairly well with the hydrazonol form stabilization that increases in isatin N-phenylsemicarbazones with electron-withdrawing substituents. Substantial difference between the Kass values for IIIa–XIa interaction with strongly and weakly basic anions allows the detection of F− or CH3COO− anions even at high weakly basic anion excess. Although mainly electron-withdrawing substituents increase the sensor sensitivity (Γ parameter), Γ increase correlates rather with the sensor ability to form 2
1 complexes correlates fairly well with the hydrazonol form stabilization that increases in isatin N-phenylsemicarbazones with electron-withdrawing substituents. Substantial difference between the Kass values for IIIa–XIa interaction with strongly and weakly basic anions allows the detection of F− or CH3COO− anions even at high weakly basic anion excess. Although mainly electron-withdrawing substituents increase the sensor sensitivity (Γ parameter), Γ increase correlates rather with the sensor ability to form 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes than with the increasing strength of electron-withdrawing group.
1 complexes than with the increasing strength of electron-withdrawing group.
Although photodegradation of IIIa–XIa E-isomer anion sensors due to light initiated E–Z isomerization can complicate anion detection, the photochemical efficiency for substituted IIIa–XIa E-isomers at 10−4 mol dm−3 concentration is even approximately 2-fold lower than for the unsubstituted Ia E-isomer, and this allows reliable detection of strong basic anions. Moreover, utilization of both E- and Z-isomers increases the F− and CH3COO− anion detection range for IIIa–XIa in organic media from approximately 5 × 10−7 to 1 × 10−4 mol dm−3 to 5 × 10−7 to 10−2 mol dm−3. A further efficient method of increasing anion detection range up to 10−3 mol dm−3 for IIIa–XIa E-isomer sensors is simultaneous sensor concentration increase and optical pathway length decrease.
Sensor VIa's low detection limit for F− anions in 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 DMF
1 DMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O mixture and the simultaneous absence of detectable CH3COO− anion levels allow confident F− detection at tolerated drinking-water fluoride level.
H2O mixture and the simultaneous absence of detectable CH3COO− anion levels allow confident F− detection at tolerated drinking-water fluoride level.
Experimental section
Synthesis
Semicarbazides were prepared using a modified procedure from the literature.24 Phenyl chloroformate (20 mmol) was added dropwise to a mixture of aniline (20 mmol), pyridine (20 mmol) and dry CH2Cl2 (40 mL) in an ice-water bath and stirred at room temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was then evaporated under reduced pressure and the residue was poured into saturated NaCl for salting out. The precipitate was filtered, dried, and stirred in hydrazine hydrate (80%, 10 ml) at room temperature for 4 hours and then filtered off and recrystallized from ethanol.General procedure
A solution of phenylsemicarbazide (6 mmol) in hot absolute EtOH (25 mL) was added to a solution of R-substituted isatine (6 mmol) in hot absolute ethanol (50 mL); R = –H (Sigma-Aldrich), –Br (Acros Organics), –OCF3 (Sigma-Aldrich) and –CH3 (Sigma-Aldrich). The reaction mixture was refluxed for 2 hours and the desired product precipitated. In the case of Xb Z-isomer, the filtrate was evaporated and the residue was purified by column chromatography using silica gel as the stationary phase and hexol (a mixture of methylpentanes and hexane; φr ∼ 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1)/ethyl acetate (φr = 2
1)/ethyl acetate (φr = 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) as the mobile phase.
3) as the mobile phase.
For further data on the synthesis and characterization of semicarbazones Ia and IIIa–XIa, see ESI Synthesis.†
Spectroscopic measurements
Electronic absorption spectra were obtained on a HP 8452A diode array spectrophotometer (Hewlett Packard, USA). The N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent was UV-spectroscopy grade (Uvasol®, Merck, Germany), and DMF was dried with CaH2 and distilled under reduced pressure. All photochemical measurements were performed at 25 °C in the dark, with only 405 nm LED diodes Thorlabs as light sources with optical power of P = 6 mW.Titration experiments
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) distilled H2O solvent mixture (φr = 9
distilled H2O solvent mixture (φr = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) at 298.16 K. The IIIa–XIa sensor solutions were titrated with the corresponding anion solutions of F−, AcO−, Br− or HSO4− to obtain 1 × 10−4 mol dm−3 or 1 × 10−5 mol dm−3 sensor concentrations of the resultant solution. The titration process in the anion concentration range of 1 × 10−5 mol dm−3 to 1 × 10−2 mol dm−3 was monitored by UV-VIS spectroscopy (in a 1 cm cuvette; 0.1 cm cuvette was used to increase the detection range).
1) at 298.16 K. The IIIa–XIa sensor solutions were titrated with the corresponding anion solutions of F−, AcO−, Br− or HSO4− to obtain 1 × 10−4 mol dm−3 or 1 × 10−5 mol dm−3 sensor concentrations of the resultant solution. The titration process in the anion concentration range of 1 × 10−5 mol dm−3 to 1 × 10−2 mol dm−3 was monitored by UV-VIS spectroscopy (in a 1 cm cuvette; 0.1 cm cuvette was used to increase the detection range).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex stoichiometry were determined using the well-known relation describing the complex anion concentration:25
1 complex stoichiometry were determined using the well-known relation describing the complex anion concentration:25
 | (1) |
For further data on the association constant for sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 1
anion 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and 2
1 and 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes, and determination of the detection and quantification limits for semicarbazones IIIa–XIa, see ESI Titration experiments.†
1 complexes, and determination of the detection and quantification limits for semicarbazones IIIa–XIa, see ESI Titration experiments.†
Light initiated E–Z isomerization
For further data on E–Z isomerization quantum yield (ΦE–Z) determination for isatinphenylsemicarbazone E-isomers IIIa–XIa in DMF solution, see ESI Light initiated E–Z isomerization.†
Appendix
A. Behaviour of the A = f(cA−) function
A = f(cA−) curve behaviour at boundary conditions (Alim = const or Kass = const, respectively) and sensor concentration of 1 × 10−4 mol dm−3 is depicted in Fig. 6 and 7. Fig. 7 shows that steepness of the A = f(cA−) curve and thus sensor sensitivity are directly linked to the Kass value for the sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 1
anion 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex describing sensor selectivity; particularly in the low Kass region. However, A = f(cA−) curve steepness does not depend on further Kass increase in the high log
1 complex describing sensor selectivity; particularly in the low Kass region. However, A = f(cA−) curve steepness does not depend on further Kass increase in the high log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Kass > 5 region. Therefore, Kass higher than 105 cannot be determined precisely by UV-VIS spectroscopy.
Kass > 5 region. Therefore, Kass higher than 105 cannot be determined precisely by UV-VIS spectroscopy.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 A = f(cA−) curve behaviour at boundary conditions (Kass = const = 1 × 106 mol−1 dm3; csensor = 1 × 10−4 mol dm−3). | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 7 A = f(cA−) curve behaviour at boundary conditions (Alim = const = 2.5; csensor = 1 × 10−4 mol dm−3). | ||
The A = f(cA−) function, described by eqn (A1),
 | (A1) |
| (c0 + 1/Kass + cA−)2 − 4c0cA− = (1/Kass − c0 + cA−)2 + 4c0/Kass. | (A2) |
Further, the bracketed term in eqn (A2) can be multiplied by unity (× [… + √ ]/[… + √ ]), which gives:
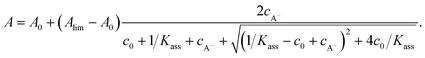 | (A3) |
Because the complex fraction on the right side of eqn (A3) is always positive for arbitrary Kass > 0, it is clear that the Alim − A0 term determines the A vs. cA− behaviour. When Alim − A0 > 0, then A is the ascending function of cA−; and vice versa.
For small cA− values (cA− → 0), eqn (A3) can be rewritten as (the complex fraction behave as x/(c0 + 1/Kass)):
 | (A4) |
Therefore, for small cA− values, the steepness of the A = f(cA−) curve directly indicating the sensor sensitivity is expressed as:
 | (A5) |
This expression clearly indicates that if the sensor concentration c0 is sufficiently higher than the inverted Kass value (c0 ≫ 1/Kass), sensor sensitivity is directly described by the (Alim − A0)/c0 ratio and does not depend on Kass value; as previously mentioned.
B. Complexities in Kass determination
The Kass value strongly depends on sensor absorbance increase at high anion concentration above 1 equivalent, despite similar slope sensitivity in the initial low concentration portion of the A = f(cA−) curve (Fig. 8).However, absorbance at anion concentration above 1 equivalent can be influenced by additional anion–sensor interactions, and these influences distort Kass value determination. For example, F− concentration above 1 equivalent leads to loss of the intramolecular hydrogen bond in the E-isomer Ia structure and simultaneous hydrazonolate C formation (ESI, Scheme S2†).16 This structural change results in hydrazonolate B absorption band hypsochromic shift in E-isomer Ia UV-VIS absorption spectra at 410 nm. However, absorbance at 410 nm further increases up to the 10 sensor equivalent and significantly affects the sensor Kass value (ESI, Fig. S12†).
This large Kass sensitivity to additional anion–receptor interactions in the high anion concentration region does not allow correct selectivity comparison for IIIa–XIa sensors from their Kass values alone. Moreover, both the lower correlation coefficient for 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex and Job's plot indicate sensor
1 complex and Job's plot indicate sensor![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) anion 2
anion 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex stoichiometry in some cases, and this further complicates IIIa–XIa Kass comparison (Table 1 and ESI, Fig. S7†).
1 complex stoichiometry in some cases, and this further complicates IIIa–XIa Kass comparison (Table 1 and ESI, Fig. S7†).
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the financial support provided by VEGA Grant Agency (Grant no. 1/1126/11).Notes and references
- P. J. Smith, M. V. Reddington and C. S. Wilcox, Tetrahedron Lett., 1992, 33, 6085–6088, DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)60012-6.
- E. Fan, S. A. van Arman, S. Kincaid and A. D. Hamilton, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 369–370, DOI:10.1021/ja00054a066.
- T. Steiner, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 48–76, DOI:10.1002/1521-3773(20020104)41:1<48::aid-anie48>3.0.co;2-u.
- M. Boiocchi, L. D. Boca, D. E. Gómez, L. Fabbrizzi, L. Licchelli and E. Monzani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 16507–16514, DOI:10.1021/ja045936c.
- M. Wenzel, M. E. Light, A. P. Davis and P. A. Gale, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 7641–7643, 10.1039/c1cc12439k.
- M. G. Chudzinski, C. A. Corey, A. McClary and M. S. Taylor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10559–10567, DOI:10.1021/ja202096f.
- G. Bergamaschi, M. Boiocchi, E. Monzani and V. Amendola, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 8276–8283, 10.1039/c1ob06193c.
- M. B. Jiménez, V. Alcázar, R. Paláez, F. Sanz, A. L. Fuentes de Arriba and M. C. Caballero, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 1181–1185, 10.1039/c1ob06540h.
- L. E. Santos-Figueroa, M. E. Moragues, E. Climent, A. Agostini, R. Martínez-Máñez and F. Sancenón, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 3489–3613, 10.1039/c3cs60316d.
- P. A. Gale, N. Busschaert, C. J. E. Haynes, L. E. Karagiannidis and I. L. Kirby, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 205–241, 10.1039/c3cs60316d.
- B. Garg, T. Bisht and S. M. S. Chauhan, Sens. Actuators, B, 2012, 168, 318–328, DOI:10.1016/j.snb.2012.04.029.
- S. L. A. Kumar, M. S. Kumar, P. B. Sreeja and A. Sreekanth, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2013, 113, 123–129, DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2013.04.103.
- S. O. Kang, R. A. Begum and K. Bowman-James, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 7882–7894, DOI:10.1002/anie.200602006.
- S. Hu, Y. Guo, J. Xu and S. Shao, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2009, 72, 1043–1046, DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2008.12.042.
- K. Jakusová, M. Cigáň, J. Donovalová, M. Gáplovský, R. Sokolík and A. Gáplovský, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2014, 288, 60–69, DOI:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2014.05.004.
- K. Jakusová, J. Donovalová, M. Cigáň, M. Gaplovský, V. Garaj and A. Gaplovský, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2014, 123, 421–429, DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2013.12.073.
- K. Jakusová, J. Donovalová, M. Gaplovský, M. Cigáň, H. Stankovičová and A. Gaplovský, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2013, 26, 805–813, DOI:10.1002/poc.3164.
- T. Gunnlaugsson, M. Glynn, G. M. Tocci (née Hussey), P. E. Kruger and F. M. Pfeffer, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2006, 250, 3094–3117, DOI:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.08.017.
- P. D. Beee and P. A. Gale, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2001, 40, 496–516, DOI:10.1002/anie.200602006.
- C. B. Rosen, D. J. Hansen and K. V. Gothelf, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 7916–7922, 10.1039/c3ob41078a.
- D. Sharma, R. K. Bera and S. K. Sahoo, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2013, 105, 477–482, DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2012.12.067.
- X. Shang, J. Yuan, Z. Du, Y. Wang, S. Jia, J. Han, Y. Li, J. Zhang and X. Xu, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2013, 96, 719–731 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Goswami, A. K. Das, D. Sen, K. Aich, H.-K. Fun and C. K. Quah, Tetrahedron Lett., 2012, 53, 4819–4823, DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.06.104.
- Y. Liu, K. Cui, W. Lu, W. Luo, J. Wang, J. Huang and C. Guo, Molecules, 2011, 16, 4527–4538, DOI:10.3390/molecules16064527.
- B. Valeur, J. Pouget, J. Bourson, M. Kaschke and N. P. Ernsting, J. Phys. Chem., 1992, 96, 6545–6549, DOI:10.1021/j100195a008.
- A. Gáplovský, Š. Toma and J. Donovalová, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2007, 191, 162–166, DOI:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.04.018.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Including additional data for Experimental section, Schemes S1 and S2, Table S1, Fig. S1–S12 and additional References. See DOI: 10.1039/c4ra04847d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |






