Enhanced photoluminescence and thermal stability of zinc quinolate following complexation on the surface of quantum dots†
Abstract
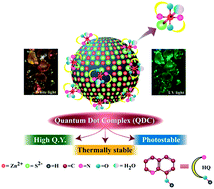
Reaction between colloidal ZnS nanocrystals (NCs) and 8-hydroxy quinoline (HQ) led to complexation on the surface of the NCs. The quantum dot complex (QDC), with ZnQ2 attached to the surface of the NC, has a longer emissive lifetime, higher fluorescence quantum yield and enhanced thermal stability, making it a better LED material than ZnQ2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...