Biocidal effect and durability of nano-TiO2 coated textiles to combat hospital acquired infections
Katarzyna Kowal*ab,
Patrick Croninb,
Ewa Dworniczekd,
Jacek Zeglinskib,
Peter Tiernanc,
Magdalena Wawrzynskad,
Halina Podbielskaa and
Syed A. M. Tofail*b
aInstitute of Biomedical Engineering and Instrumentation, Wroclaw University of Technology, Wybrzeze Wyspianskiego 27, 50-370 Wroclaw, Poland. E-mail: katarzyna.kowal@pwr.edu.pl; Fax: +48 (71)327 77 27; Tel: +48 (71)320 65 80
bDepartment of Physics and Energy, Materials and Surface Science Institute, University of Limerick, Ireland. E-mail: tofail.syed@ul.ie
cDepartment of Design and Manufacturing Technology, Materials and Surface Science Institute, University of Limerick, Ireland
dDepartment of Microbiology, Medical University of Wroclaw, Chalubinskiego 4, 50-368 Wroclaw, Poland
First published on 16th April 2014
Abstract
While antimicrobial textiles have received considerable interest and attention from both the scientific community and general consumers, there have been very few studies investigating the durability of such antimicrobial activities. In this study, we describe the modification of the surface of textiles that were modified with commercially available titanium dioxide (TiO2) powder (P25 Aeroxide®, Degussa™) using a sonochemical technique. The antibacterial activity of TiO2 can improve textile quality and effectively reduce the rate of infections acquired in hospitals. Medical garments produced from such fabrics may improve the patient's recovery and revolutionize the textile market. This modification imparts biocidal properties to these textiles, which were then optimized to acquire properties of the textile. Samples were washed for 30 cycles at three different temperatures (40 °C, 60 °C and 90 °C) to test the durability of the bonding of the nanoparticles to textiles and the effectiveness was examined with respect to their antimicrobial activity against hospital pathogens: Escherichia coli, MRSA and Candida albicans. Sample's surfaces were examined by a Scanning Electron Microscope equipped with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) for surface imaging. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS) was used as a technique to quantify the Ti present on the fabric. The best durability of TiO2 on textiles was best retained after washing at 40 °C. From an environmental point of view, the release of nanomaterial from textiles was acceptable against currently available benchmarks. We have investigated the adhesion of nanoparticles (NPs) to the textile surface. Medical garments, bed linens and upholstery produced from such fabrics may improve hospital hygiene against antibiotic resistant superbugs and help reduce hospital acquired infections.
1. Introduction
Due to antibiotic resistance, common infection type bacteria, nosocomial, or the so called hospital-acquired infections (HAI) are on the rise. It has been reported that 10% of patients are infected in the hospital due to HAI.1 There are many examples of bacteria species which are the source of HAI, but methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is commonly the most difficult microbe to treat by common antibiotics.2 Hygiene practices such as washing hands3 have received only a limited success in restricting the spread of such HAI's, as the reduction of the prevalence of such infections is difficult.4 The pathways and risk factors of bacteria transmission include infection via medical devices by catheters, sensors, but also contact between personnel, patients, and contact with contaminated surfaces in the operation theatre (handles, platforms, panels), and transfer by medical garments, bedclothes, and curtains.5,6 Antibacterial textiles that can kill pathogenic microorganisms will ipso facto reduce the occurrence of hospital acquired infections (HAI).7Antibacterial NPs can be used as active biocidal agents to impart antimicrobial properties in textiles.6 NPs are finding applications in fields that range from cosmetics to electronics.8 There are several types of NP that can potentially be used as killing agents for microbes: zinc oxide (ZnO), carbon nanotubes (CNT), copper (Cu) and copper oxide (CuO), silver (Ag) materials and titanium dioxide (TiO2).9–11 On the other hand, there are several commercially available antimicrobials for textile applications including triclosan, ammonium compounds, zinc pyrithione and, recently, silver and nanosilver.12,13
Among these possible biocidal agents, the main advantage of nano-TiO2 is the ability to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a result of photo-activated reactions.14–17 The ROS produced after absorption of radiation from the UV range give titania its antimicrobial activity.18–20 This property of titania nanomaterials can be exploited to improve the properties of a textile surface.
In the last decade, there have been many examples of the improvement of quality and potential functions where fabrics benefit from nanotechnology to produce breathable, waterproof, and flame-resistant textiles.21,22 Various methods have been used to add nanomaterials to textiles, including: dip-coating;23–25 pad-dry-cure method;26–28 and methods involving plasma modification.29–31 Among these methods, it was reported that NP's can be incorporated into textile surfaces through a sonochemical process. Efficiency of this method arises from acoustic cavitation: formation and collapse of bubbles. It has been extensively developed and published by Perelshtein, Abramov and Gedanken.32–35 It was proven that there was an antibacterial effect of CuO and ZnO against several bacteria species on textiles modified using a sonochemical technique. Ultrasonic modification of textiles was lately published by Montazer36 to photo bleach wool surface.
Here we impart a biocidal activity onto textiles by modifying them with commercially available NPs of titania using a sonochemical technique (dip coating with simultaneous ultrasonic treatment). We then investigated the durability, adhesion and biocidal activity of these fabrics.
Efficient durability of NPs impregnated fabrics is an important characteristic of washable and reusable antimicrobial textile articles.37 Surprisingly, this characteristic of reusable antimicrobial textiles has been overlooked in the literature. The durability and adhesion of NPs to textiles are significant issues related to workers and consumer safety from potential hazards of exposure to NPs.38 Standard methods for testing durability based on colour fastness analysis using appropriate greyscale39 or spectroscopy in UV-Vis spectral range.40 As antimicrobial properties of NPs treated textiles originate from the presence of the NPs on the textile surface, the durability of NPs adhesion to textiles also signifies the durability of the antimicrobial properties. Assessing from an environmental standpoint, colour fastness tests using washing procedures can examine the strength of adhesion as well as the potential effluence of NPs in a waste water stream. In this study, we have also tested the adhesion of NPs by using a modified coating adhesion test. The durability and efficacy of the sonochemical treatment of textiles were then tested against Gram positive bacteria, Gram negative bacteria and fungi using standardized antimicrobial test procedures for textiles. Such investigations have allowed us to test the biocidal effect of textiles against a full spectrum of common microbes and were therefore helpful to examine the general broad spectrum antimicrobial activity of these textiles.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles with PET textiles
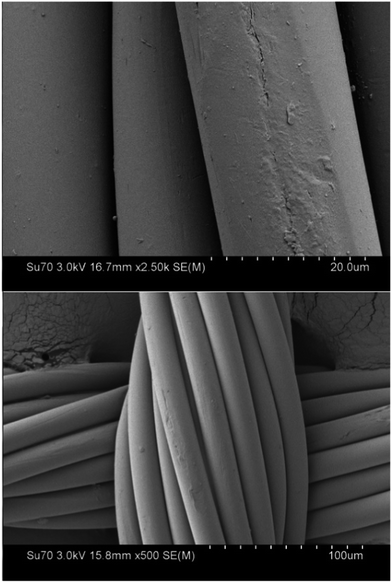
For this study, 100% polyethylene terephthalate (PET) textile was used (50 g m−2, 130/130 warp/weft density). The SEM pictures of textiles are presented on Fig. 1. A single fibre is of 20 μm diameter and the thread diameter is ∼100 μm. To remove impurities from the textile surface, samples were pre-treated in acetone (acetone pure p.a. 99.5% Polish Chemical Reagents) for 10 min on a magnetic stirrer (3000 rpm) and dried at a temperature of 70 °C in the laboratory oven (Pol-Eko, SLW STP 53).Textiles were impregnated in a water sol of TiO2 (5 g l−1) of commercially available P25 powder (Aeroxide® P25 Degussa Evonik).41 Solution was mixed for 1 hour using a magnetic stirrer. Textile samples were dip-coated in TiO2 solution, and then heated to 50 °C and sonicated for 5 min in an ultrasonic washer (InterSonic IS-1K). The samples were then dried at 70 °C (Pol-Eko, SLW STP 53).
2.2. Durability testing method
Standard methods of testing durability of textiles are listed in AATCC Test Method 61-2013 (ref. 39) and ISO 105-C06:2010.42 The colorfastness tests are accelerated methods used to evaluate loosing of color of textiles which are expected to withstand frequent laundering. One such test takes about 45 min and the action (detergent solution and abrasive action) represents that of five typical home launderings. In our approach, washing of textiles was performed at washing temperature settings of: 40 °C, 60 °C and 90 °C. A magnetic stirrer was used to agitate the wash water, using a heating setup and thermocouple to provide and monitor the water temperature. A 400 ml volume of distilled water was heated to a set temperature, and the magnetic stirrer motor was set at 3000 rpm, where the textile samples were immersed for 10 min. This washing procedure was a simplified washing method, using laboratory-available equipment, which we have used to study the impact of temperature on NPs retention. This washing is equivalent to one domestic cycle of washing. After this process, the textiles were dried at 70 °C. The washing procedure was performed for a maximum of 30 cycles.2.3. Atomic absorption spectrometry
The concentration of Ti on textiles was determined by using atomic absorption spectrometry using a modified version of ASTM 4563-02.43 Textiles were analyzed using a Spectra AA 200 Spectrometer fitted with a hallow cathode lamp containing a Ti element with a wavelength of 364.3 nm. Textiles were cut into 16 cm2 square-shaped samples, and transferred to 50 ml flasks, where they were dissolved in hydrofluoric acid (HF) 48% AR supplied by Scientific & Chemical Supplies Ltd. and then rinsed in distilled water. The concentration of Ti was quantified by AAS in an airy acetylene and nitrous oxide flame using an aqueous standard calibration curve. The Ti standard used for the examination was purchased from Inorganic Ventures.2.4. Adhesion assessment
The adhesion of a nanomaterial to a textile surface, and the durability of immobilization of the NPs have been significantly researched as important issues regarding the release of nanomaterials into the environment. The adhesive strength was examined using a modified pull-off method according to ASTM D4541.44 The quantity of titania remaining on the sample surfaces was measured using low magnification Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS).2.5. Antimicrobial assay
Antimicrobial tests were performed using clinical strains of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) K 324 and Escherichia coli PA 170, the reference strain of yeasts Candida albicans ATCC 90028 and the fabrics impregnated with TiO2 NPs, both unwashed and after 30 cycles of washing, at temperature settings of 40, 60 and 90 °C.The inoculated samples were subjected to UVA irradiation using a Wood's lamp set at λmax = 365 nm, GP = 1.5 mW cm−2, and irradiation times set at 20, 40 and 60 min. The selection of 365 nm was dictated by the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 activity in UV-A range.46 The power, 1.5 mW cm−2 was used to mimic the terrestrial intensity of UVA radiation in typical solar spectra. Analogous systems were stored in a dark environment, with no exposure to any type of light wavelength. Additionally, a benchmark antimicrobial test for an unmodified polyester fabric was washed and illuminated in the aforementioned conditions. After exposure, the cultures were diluted and spread onto Tryptic Soy agar plates. The colony forming units were counted after incubation for 24–48 hours at 37 °C. The percentage reduction of bacteria (R) was calculated as follows:
| R = 100(C − A)/C | (1) |
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Preparation of TiO2 modified polyester
NPs of TiO2 were deposited on polyester fabrics. The concentration of Ti on samples was measured by means of AAS and low magnification EDS. The coverage of nanoparticles on textile yarn surfaces at higher magnification of SEM are presented in Fig. 2, which shows that the textiles were successfully covered with NPs of TiO2 but this coverage is dispersed and does not form a continuous film on the fibre. In the sonochemical deposition process, cavitation microjets and waves can drive particles with sufficiently high velocities so as to cause fusion of NPs onto the textile surface where the particles can adhere strongly to the surface during particle–substrate collision.48,49 The nanomaterial covered the majority of the outer surface of the yarn, but there were also NPs in the voids between the yarns. The coverage was non-homogenous, and the NPs agglomerated and formed clusters. These agglomerates were typical for P25 powder.50 Due to the nature of substrate51 NPs are bonded to fabric through van der Waals bonding.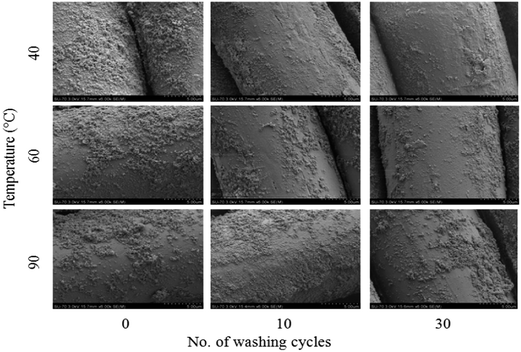 | ||
| Fig. 2 Scanning electron micrographs of the morphology of PET textile fibres after sonochemical modification with nanotitania followed by an accelerated washing for 0, 10 and 30 cycles at 40 °C, 60 °C, 90 °C. For quantitative analysis of the retention of nanoparticles please see Fig. 3. | ||
However the distribution of NPs had an influence on properties and activity of the prepared material. On yarns, there were areas with a dense accumulation of TiO2 and there were also areas of surface with no visible presence of NPs.
3.2. Durability and washing
3.3. Adhesion test
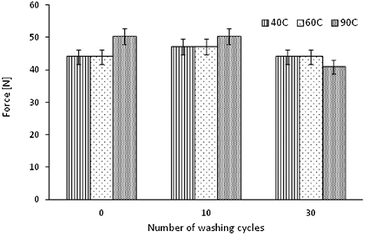
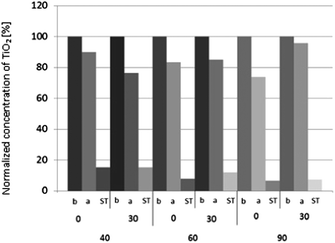
In this research, a conventional test method was used to analyze the long-term adhesion of NPs to textile surfaces. The pull-off test method was used for this assessment, and allows for the examination of the force required to remove an adhered dolly from a textile surface.Fig. 5 shows that about 10 to 20% of initial TiO2 on textiles was removed with the adhesive-tape. Values obtained for samples after 30 cycles of wash, do not differ from the non-washed samples. It is inconclusive if one set of washing conditions affects the adhesion of NPs, as the outcomes were similar for all samples. There is still better retention of NP's after 30 cycles of washing compared to 0 cycles of washing because the washing procedure removes the loosely bound NP's from the fabric. The NP's retained on the fabric after washing are strongly bound NP's. Proportions between the samples before pull-off test and the sum of titania after pull-off testing, and present on the adhesive tape were mostly preserved. This result does not provide a conclusive indication of adhesion of NPs. There was an important aspect to the properties of the adhesive tape and the potential impact on the adhesion test results.
3.4. Microbiological assay
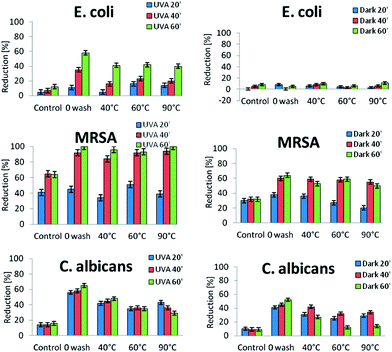
Antibacterial tests were performed for MRSA, Escherichia coli and fungi Candida albicans. Those strains were selected as they were common in nosocomial testing area.1,5–7 Textile samples were irradiated with UVA and stored in dark conditions for 20, 40 and 60 minutes (Fig. 6).It was observed that PET textile has bacteriostatic properties (see control sample in Fig. 6). Moreover, after irradiation with UVA, the antibacterial activity increased. After 20 min of UVA irradiation, approximately 40% of colonies were killed, and for increased irradiation times, the bacterial reduction rate was even larger at 60%.
Antimicrobial activity of TiO2 modified textiles was obtained for all tested bacteria strains and fungi. The weakest effect was detected for strains of E. coli. For the samples stored in dark conditions, the mean reduction of bacteria was 10%. The best microbial results were obtained for samples washed at 40 °C. The optimal distribution of NPs was assumed to be the major reason for obtaining better antibacterial effect. Textiles impregnated with nano-TiO2 using a modified ultrasonic method, showed a 20% microbial reduction after 20 min of UVA irradiation, and almost 40% of reduction after 40 min of irradiation. After 1 hour of irradiation, at least 60% of E. coli colonies were killed on unwashed samples. Even after 30 cycles of washing, the antibacterial activity of the textile was maintained. Although nanomaterials were released during the wash process, antibacterial activity of 40% was still achieved. Antimicrobial tests for E. coli and C. albicans clearly indicated reducing biocidal effects with washing. When comparing data obtained for samples washed at three temperature settings, the best results for killing E. coli were obtained for samples washed at 60 °C.
Textiles revealed an inherent antibacterial activity, and when an antimicrobial NPs were added, the activity against microbes was further strengthened. Another way to increase the biocidal activity was to irradiate the textile samples. Improved activity was obtained against C. albicans. The antifungal effect on textiles was better than that assessed against E. coli. A longer incubation time initiated an increased biocidal effect, even when textiles were stored in dark conditions. The effect was slightly decreased after NPs reduction by washing, but remained efficient for microbial activity. In the case of C. albicans incubated in dark conditions, the most effective results were observed after 40 min of incubation. Irradiation of textile samples enhanced the antimicrobial activity. Results show that the irradiation time had no significant influence on the biocidal effect. Here the results obtained for textile samples incubated with C. albicans with the presence of UVA for 20, 40 or 60 min were comparable, and presented 60% reduction on the unwashed sample. After washing, the activity of textiles decreased and the best result remained for the samples washed at 40 °C.
The largest biocidal effect was observed on the MRSA strain, a result which was considered significant to the study. Loading TiO2 onto a textile surface using an ultrasonic process produced textiles capable of reducing MRSA by 40–60%, where incubation time was a dependent factor. Washing textile samples did not significantly influence the antibacterial activity against MRSA, where results obtained for samples incubated for 20 min decreased, and after 40 min they were significantly similar to those assessed for unwashed textiles. Using 60 min of incubation and UVA irradiation, almost 100% of MRSA was killed. It was noted that washing did not affect the antibacterial activity of textiles. The proposed method enabled significant biocidal activity of pathogenic MRSA from various hospital settings.
4. Discussion
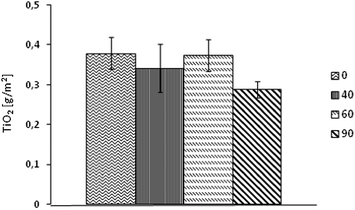
In this paper it was demonstrated that textiles can be coated with NPs of TiO2 using an ultrasonic surface modification process. This is a novel technique, where efficacy using a sonochemical modification of textiles was presented for other functional oxides.32–35 The SEM images showed that the obtained NP layer was not continuous over the textile surface and that the TiO2 formed aggregates. The distribution of NPs was random and non-homogenous, as it has been previously observed and reported.32–35 There were areas where accumulation of NPs was dense, while some other surfaces had no coverage of NPs. The SEM images showed that NPs were adhered to the yarn surface, and that they were durable to fibres even after 30 cycles of washing. This effect was revealed for three washing temperature settings. The aggregates of TiO2 remained on textile surfaces even after several washing cycles, they are believed to be less harmful to the environment than NPs that have not been exposed to a light source.55,56 It was assumed that the NPs released during the washing process have originated from the outer surface of the yarns, while the remaining NPs accumulated in the voids between fibres. Detailed information on the Ti content on PET textiles was assessed using AAS, where it revealed that the highest Ti content on textiles was from samples washed for 30 cycles at a temperature of 40 °C. According to the toxicity of TiO2 the dislodgement of NPs from a textile surface was lower than 1 ppm per wash cycle, which meets the recommended safety requirements of NP exposure of titania.57,58 The maximum release of NPs was observed for samples washed at 90 °C (0.17 ppm per cycle).Standard pull-off testing methods were used to assess the adhesion properties of NP layers to textile surfaces – where a similar application of these tests for the adhesion characterization of TiO2 coatings has been studied.59 However, these testing techniques can also be applied in testing mechanical properties of textiles. Outcomes from the adhesion test in this study showed that there was no significant difference in the pull-off strength between unwashed samples and the samples washed at 10 or 30 cycles at 40 °C, 60 °C, 90 °C. After the pull-off tests, the textile surfaces were examined using an EDX analyzer. The Ti content was studied on samples before and after the pull-off test, and on the adhesive tape used in the test. It was expected that the Ti content on samples before the pull-off test would be equal to the Ti content on the sample after the test, and when added to the Ti content from the adhesive tape. Experimental results were in agreement with the proposed hypothesis. The content of Ti on samples before the pull-off test was marginally different, and proved that this technique of coating allows the loading of fabric with approximately 35–45% of a inhomogeneous layer. Analysis of the adhesive tape revealed that about 20% of the initial Ti was pulled-off from the fabric surface, revealing that the NPs were durable to the fabric. Furthermore after 30 cycles of washing, the content of Ti that was pulled-off from the fabric was lower than the unwashed fabrics.
Antimicrobial test showed that the textiles revealed inherent bactericidal properties. This inherent activity can add to the already instilled biocidal activity from applying a NP surface coating. Adding NPs of TiO2 to the textiles significantly improved the antimicrobial activity, and also with the addition of UVA irradiation the biocidal effect was further influenced. The highest antimicrobial activity of coated textiles was revealed against strains of MRSA. As reported, the NPs of TiO2 have the ability to suppress the growth of several bacteria.18,28,60–62 The higher effectiveness of TiO2 against MRSA than compared against Gram-negative bacteria was considered to be a factor of the complexity and differences in the cell walls of different bacteria that that have various resistance to nanomaterials.20 An extension of the antimicrobial activity of modified textiles against a broader spectrum of organisms can be implemented by applying NPs of TiO2 doped with silver.
5. Conclusions
By conducting several experiments to assess the modification of synthetic textiles with antimicrobial agents at the nano-scale, commercially available TiO2 was coated to the surfaces of polyester fabrics providing an effectively covered surface using an ultrasonically enhanced process. The durability of the prepared samples was the best after washing in 40 °C, noting that they were below the recommended environmental requirements, the release of the nanomaterial was within the acceptable limits. We have made an attempt to understand the adhesion of NPs to the textile surface, using a normalized testing mechanism, which to date far has only been used for flat surfaces. The photoactive fabrics showed antimicrobial activity against E. coli, C. albicans and MRSA, which are significantly responsible towards hospital infections. Textiles having the listed properties can effectively improve the quality of care in medical-care environments.Acknowledgements
The BioElectricSurface research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2011) under grant agreement no. 212533. This communication reflects the views only of the author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.Notes and references
- World Health Organization. Prevention of hospital-acquired infections: A practical guide. WHO/CDS/CSR/EPH/2002.12 2002, 1–64, accessed 7 October 2013, http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/drugresist/en/whocdscsreph200212.pdf.
- J. T. Murohy, R. Walshe and M. Devocelle, J. Theor. Biol., 2008, 254, 284–293 Search PubMed.
- A. Kendall, T. Landers, J. Kirk and E. Young, Am. J. Infect. Control, 2012, 40, S3–S10 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. D. Bartels, K. Kristoffersen, T. Slotsbjerg, S. M. Rohde, B. Lundgren and H. Westh, J. Hosp. Infect., 2008, 70, 35–41 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Kowal, S. A. M. Tofail and H. Podbielska, How to prevent hospitalized patients from harmful nosocomial infections?, in Acta Biomedical Engineering, Nutraceutics, Biomedical remedies and physiotherapeutic methods for prevention of civilization-related disease, Indygo Zahir Media, Wroclaw, 2011, pp. 255–262 Search PubMed.
- J. Bauer, K. Kowal, S. A. M. Tofail and H. Podbielska, MRSA-resistant Textiles, in Biological Interaction with Surface Charge in Biomaterials, Royal Society of Chemistry Publishing, Cambridge, 2012, pp. 193–207 Search PubMed.
- G. Borkow and J. Gabbay, Med. Hypotheses, 2008, 70, 990–994 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Sang, L. Zheng, Q. Sun, N. Li, Y. Cui, R. Hu, G. Gao, Z. Cheng, J. Cheng, S. Gui, H. Liu, Z. Zhang and F. Hong, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A, 2012, 100, 894–902 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zou, D. Li, X. Sheng, L. Wang and D. Yang, Sol. Energy, 2012, 86, 1359–1365 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Synnott, M. Seery, S. Hinder, G. Michlits and S. Pillai, Appl. Catal., B, 2013, 130–131, 106–111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Sataev, S. T. Koshkarbaeva, A. B. Tleuova, S. Perni, S. B. Aidarova and P. Prokopovic, Colloids Surf., A, 2014, 442, 146–151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Winler, M. Height and B. Nowack, Environ. Int., 2013, 53, 62–73 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Piccinno, F. Gottschalk, S. Seeger and B. Nowack, J. Nanopart. Res., 2012, 14, 1109 CrossRef.
- K. Nakata and A. Fujishima, J. Photochem. Photobiol., C, 2012, 13, 169–189 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Di Paola, G. Cufalo, M. Addamo, M. Bellardita, R. Campostrini, M. Ischia, R. Ceccato and L. Palmisano, Colloids Surf., A, 2008, 317, 366–376 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Taranto, D. Frochot and P. Pichat, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2009, 67, 187–193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Bai, L. Liu, Z. Liu and D. D. Sun, Water Res., 2013, 47, 4126–4138 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Markowska-Szczupak, K. Ulfig and A. W. Morawski, Catal. Today, 2011, 169, 249–257 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. T. Vu and K. Won, Food Chem., 2013, 140, 52–56 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Kowal, K. Wysocka-Krol, M. Kopaczynska, E. Dworniczek, R. Franiczek, M. Wawrzynska, M. Vargova, M. Zahoran, E. Rakovsky, P. Kus, G. Plesch, A. Plecenik, F. Laffir, S. A. M. Tofail and H. Podbielska, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 362, 50–57 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Moczulska, M. Bitar, W. Swieszkowski and A. Bruinink, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A, 2012, 100, 882–893 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gugliuzza and E. Drioli, J. Membr. Sci., 2013, 446, 350–375 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Yuranova, R. Mosteo, J. Bandara, D. Laub and J. Kiwi, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2006, 244, 160–167 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. T. Meilert, D. Laub and J. Kiwi, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2005, 237, 101–108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Harifi and M. Montazer, Dyes Pigm., 2013, 97, 440–445 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Sójka-Ledakowicz, J. Lewartowska, M. Kudzin, M. Leonowicz, T. Jesionowski, K. Siwinska-Stefanska and A. Krysztafkiewicz, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44, 3852–3800 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Selvam, R. Rajiv Gandhi, J. Suresh, S. Gowri, S. Ravikumar and M. Sundrarajan, Int. J. Pharm., 2012, 43, 4366–4374 Search PubMed.
- W. Kangwansupamonkon, V. Lauruengtana, S. Surassmo and U. Ruktanonchai, Nanomedicine, 2009, 5, 240–249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. M. Walk, J. A. Snyder, P. Srinivasan, J. Kirsch, S. O. Diaz, F. C. Blanco, A. Shashurin, M. Keidar and A. D. Sandler, J. Pediatr. Surg, 2013, 48, 67–73 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Vaideki, S. Jayakumar, R. Rajendran and G. Thilagavathi, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2008, 254, 2472–2478 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Vesel, M. Mozetic, S. Strnad, Z. Persin, K. Stana-Kleischek and N. Hauptman, Vacuum, 2010, 84, 79–82 CrossRef PubMed.
- O. V. Abramov, A. Gedanken, Y. Koltypin, N. Perkas, I. Perelshtein, E. Joyce and T. J. Mason, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 204, 718–722 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Perelshtein, G. Applerot, N. Perkas, E. Wehrschetz-Sigl, A. Hasmann, G. M. Guebitz and A. Gedanken, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2009, 1, 361–366 CAS.
- I. Perelshtein, G. Applerot, N. Perkas, E. Wehrschetz-Sigl, A. Hasmann, G. M. Guebitz and A. Gedanken, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 204, 54–57 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Abramova, A. Gedanken, V. Popov, E. Ooi, T. J. Masond, E. Joyce, J. Beddow, I. Perelshtein and V. Bayazitov, Mater. Lett., 2013, 96, 121–124 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Montazer and S. Morshedi, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2014, 20, 83–90 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Perera, B. Bhushan, R. Bandara, G. Rajapakse, S. Rajapakse and C. Bandara, Colloids Surf., A, 2013, 436, 975–989 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mullins, F. Murphy, L. Baublyte, E. M. McAlea and S. A. M. Tofail, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2013, 8, 222–224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists. AATCC Test Method 61-20013, Colorfastness to Laundering: Accelerated, 2013.
- F. A. Sadr and M. Montazer, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2014, 21, 681–691 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Bozzi, T. Yuranova, I. Guasaquillo, D. Laub and J. Kiwi, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2005, 174, 156–164 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- International Organization for Standardization, ISO 105–C06:2010, Textiles – Tests for colour fastness- Part C06: Colour fastness to domestic and commercial laundering, 2010.
- American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM D 4563–02(2008) Standard Test Method for Determination by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy of Titanium Dioxide Content of Pigments Recovered From Whole Paint, 2008.
- American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM D 4541-95 Standard Test Methods for Pull-Off Strength of Coatings using Portable Adhesion Testers, 1995.
- N. M. M. Ramos, M. L. Simões, J. M. P. Q. Delgado and V. P. de Freitas, Construct. Build. Mater., 2012, 31, 86–93 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. M. Kang, B. L. Yuan, J. G. Xu and M. Fu, Catal. Lett., 2011, 141, 1371–1377 CrossRef CAS.
- American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists. AATCC 100-2004 Antimicrobial Fabric Test Assessment of Antibacterial Finishes on Textiles, 2004.
- K. S. Suslick and G. J. Price, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1999, 29, 295–326 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Soloviev and A. Gedanken, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2011, 18, 356–362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yu, H. Yu, B. C. Minghua Zhou and X. Zha, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2006, 253, 112–118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. V. Abramov, A. Gedanken, Y. Koltypin, N. Perkas, I. Perelshtein, E. Joyce and T. J. Mason, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 204, 718–722 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. MacNamara, A. Gabriele, C. Amador and S. Bakalis, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2012, 75, 14–27 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Jurando, V. Bravo, G. Luzon, M. Fernandez-Serrano, M. Garcia-Roman, D. Altmajer-Vaz and J. M. Vicaria, J. Surfactants Deterg., 2007, 10, 61–70 CrossRef.
- T. Paul, A. Das, A. Mandal, S. K. Halder, A. Jana, C. Maity, P. K. DasMohapatra, B. R. Pati and K. C. Mondal, J. Cleaner Prod., 2014, 66, 672–684 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. French, A. R. Jacobson, B. Kim, S. L. Isley, R. L. Penn and P. C. Baveye, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43, 1354–1359 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Tong, C. Binh, J. Kelly, J. Gaillard and K. Gray, Water Res., 2013, 47, 2352–2362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Occupational Exposure to Titanium Dioxide. Current Intelligence Bulletin, 2011, 63, 1–119.
- L. K. Adams, D. Y. Lyon and P. J. J. Alvarez, Water Res., 2006, 40, 3527–3532 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. A. Al-Turaif, Prog. Org. Coat., 2010, 69, 241–246 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Bodaghi, Y. Mostofi, A. Oromiehie, Z. Zamani, B. Ghanbarzadeh, C. Costa, A. Conted and M. A. Del Nobile, Food Sci. Technol., 2013, 50, 702–706 CAS.
- K. P. Kuhn, I. F. Chaberny, K. Massholder, M. Stickler, V. W. Benz, H. Sonntag and L. Erdinger, Chemosphere, 2003, 53, 71–77 CrossRef CAS.
- C. M. Hessler, M. Wu, Z. Xue, H. Choi and Y. Seo, Water Res., 2012, 46, 4687–4696 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |