Nanostructured CuO/reduced graphene oxide composite for hybrid supercapacitors†
Abstract
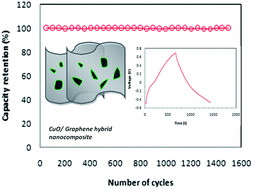
To address the issues such as low ionic conductivity, poor electrode kinetics and cyclic stability, the strategy of combining carbon-based materials with transition metal oxide (TMO) is adopted. In this article, the preparation of CuO/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanocomposite electrodes by a simple, low cost hydrothermal method is described. This hybrid nanocomposite exhibits a high specific capacitance of 326 F g−1 at a current density of 0.5 A g−1. It shows a high energy density of 65.7 W h kg−1 at a power density of 302 W kg−1. Further, this material does not exhibit any measureable degradation in electrochemical performance, even after 1500 cycles. Symmetric hybrid capacitors exhibit a specific capacitance of 97 F g−1 at 0.2 A g−1 with a power density of 72 W kg−1. These superior electrochemical features demonstrate that the CuO/RGO hybrid nanocomposite is a promising material for next-generation supercapacitor systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...