Core–shell ZnSe–CdSe quantum dots: a facile approach via decomposition of cyclohexeno-1,2,3-selenadiazole†
Abstract
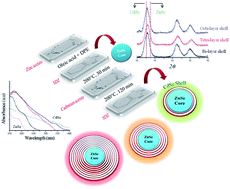
For the first time ever cyclohexeno-1,2,3-selenadiazole (SDZ) has been employed for the synthesis of core–shell ZnSe–CdSe quantum dots thus promoting an eco-friendly and reasonably less toxic synthesis method for such quantum dot hetero-structures. The synthesized dark-red colored core–shell structures were characterized by UV-Visible and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy to examine their band-gap. The absorption and emission spectra also showed gradual red-shifts in wavelength with respect to zinc selenide (core). Also, the band-gap of such core–shell quantum dots can be tuned by varying the shell layer thickness and/or particle size. The findings from the XRD analysis, near-to-homogenous particle size distribution, formation of a decent nano-crystalline product and a good agreement with Vegard's law, signify that the present synthesis approach could be highly effective for the precise tailoring of core–shell QDs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...