Structures and properties of four coordination polymers constructed from 1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane and aromatic dicarboxylic acids†
Abstract
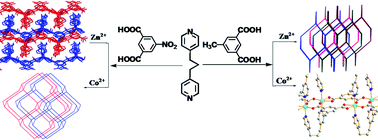
Four coordination polymers associated with 1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl) propane (bpp) and 5-methylisophthalic acid (H2mip) or 5-nitroisophthalic acid (H2nip) formulated as [Zn(bpp)(mip)]n (1), [Co(bpp)(mip)]n (2), [Zn2(bpp)2(nip)2]n (3) and [Co(bpp)(nip)(H2O)]n (4) have been synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. Single crystal analyses reveal that complex 1 presents a four-fold interpenetrating framework based on three-dimensional (3D) subunits with dia topology. Compound 2 has a 1D binuclear chain structure. Complex 3 shows 2D 44-sql layer structure packing in ABAB mode. Complex 4 exhibits a two-fold interpenetrating framework based on three-dimensional (3D) subunits with dia topology. These compounds have been characterized by infrared spectroscopy, elemental analysis, thermogravimetric analysis and powder X-ray diffraction. In addition, the photoluminescence of 1 and 3 and magnetic properties of 2 and 4 were investigated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...