A new mechanistic approach to elucidate furosemide electrooxidation on magnetic nanoparticles loaded on graphene oxide modified glassy carbon electrode†
Abstract
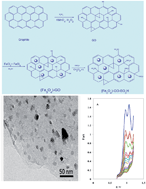
The electrochemical behavior of furosemide was investigated at the magnetic graphene oxide functionalized by chlorosulfonic acid-modified glassy carbon electrode (Fe3O4-GO-SO3H-GCE) in phosphate buffer solution (PBS), pH 6.8. Cyclic voltammetric study indicated that the oxidation process is irreversible and diffusion controlled. The number of exchanged electrons in the electro-oxidation process was obtained, and the data indicated that furosemide is oxidized via two one-electron steps. The results revealed that Fe3O4-GO-SO3H promotes the rate of oxidation by increasing the peak current. The diffusion coefficient and electron-transfer coefficient of furosemide were found to be 2.18 × 10−6 cm2 s−1 and 0.46, respectively. A sensitive, simple and time-saving differential-pulse voltammetric procedure was developed for the analysis of furosemide. The results show that by using the proposed method, furosemide can be determined with a detection limit of 0.11 μM. Finally, the applicability of the method to direct assays of spiked human serum and urine fluids is described.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...