Fluoro-polymer functionalized graphene for flexible ferroelectric polymer-based high-k nanocomposites with suppressed dielectric loss and low percolation threshold†
Abstract
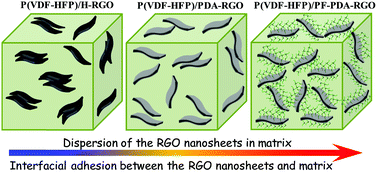
Flexible nanodielectric materials with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss have huge potential applications in the modern electronic and electric industry. Graphene sheets (GS) and reduced-graphene oxide (RGO) are promising fillers for preparing flexible polymer-based nanodielectric materials because of their unique two-dimensional structure and excellent electrical and mechanical properties. However, the easy aggregation of GS/RGO significantly limits the potential of graphene in enhancing the dielectric constant of polymer composites. In addition, the poor filler/matrix nanoscale interfacial adhesion also causes difficulties in suppressing the dielectric loss of the composites. In this work, using a facile and environmentally friendly approach, polydopamine coated RGO (PDA-RGO) and fluoro-polymer functionalized RGO (PF-PDA-RGO) were prepared. Compared with the RGO prepared by the conventional methods [i.e. hydrazine reduced-graphene oxide (H-RGO)] and PDA-RGO, the resulting PF-PDA-RGO nanosheets exhibit excellent dispersion in the ferroelectric polymer matrix [i.e. poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoro propylene), P(VDF-HFP)] and strong interfacial adhesion with the matrix, leading to a low percolation threshold (fc = 1.06 vol%) and excellent flexibility for the corresponding nanocomposites. Among the three nanocomposites, the P(VDF-HFP)/PF-PDA-RGO nanocomposites exhibited the optimum performance (i.e. simultaneously having high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss). For instance, at 1000 Hz, the P(VDF-HFP) nanocomposite sample with 1.0 vol% PF-PDA-RGO has a dielectric constant of 107.9 and a dielectric loss of 0.070, showing good potential for dielectric applications. Our strategy provides a new pathway to prepare high performance flexible nanodielectric materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...