Gelatin functionalized graphene oxide for mineralization of hydroxyapatite: biomimetic and in vitro evaluation†
Abstract
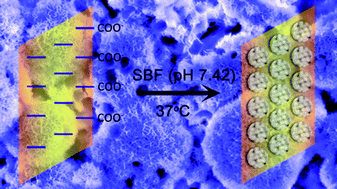
We report a facile modification of graphene oxide (GO) by gelatin to mimic charged proteins present in the extracellular matrix during bone formation. The bioinspired surface of GO–gelatin (GO–Gel) composite was used for biomimetic mineralization of hydroxyapatite (HA). A detailed structural and morphological characterization of the mineralized composite was performed. Additionally, MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured on the GO–Gel surfaces to observe various cellular activities and HA mineralization. Higher cellular activities such as cell adhesion, cell proliferation, and alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) were observed on the GO–Gel surface compared with the GO or glass surface. The increase of ALP confirms that the proposed GO–Gel promotes the osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells. Moreover, the evidence of mineralization evaluated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and alizarin red staining (ARS) corroborate the idea that a native osteoid matrix is ultimately deposited. All these data suggest that the GO–Gel hybrids will have great potential as osteogenesis promoting scaffolds for successful application in bone surgery.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...