Interference of CuO nanoparticles with metal homeostasis in hepatocytes under sub-toxic conditions†
Abstract
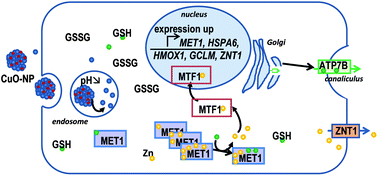
Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NP) were studied for their toxicity and mechanism of action on hepatocytes (HepG2), in relation to Cu homeostasis disruption. Indeed, hepatocytes, in the liver, are responsible for the whole body Cu balance and should be a major line of defence in the case of exposure to CuO-NP. We investigated the early responses to sub-toxic doses of CuO-NP and compared them to equivalent doses of Cu added as salt to see if there is a specific nano-effect related to Cu homeostasis in hepatocytes. The expression of the genes encoding the Cu-ATPase ATP7B, metallothionein 1X, heme oxygenase 1, heat shock protein 70, superoxide dismutase 1, glutamate cysteine ligase modifier subunit, metal responsive element-binding transcription factor 1 and zinc transporter 1 was analyzed by qRT-PCR. These genes are known to be involved in response to Cu, Zn and/or oxidative stresses. Except for MTF1, ATP7B and SOD1, we clearly observed an up regulation of these genes expression in CuO-NP treated cells, as compared to CuCl2. In addition, ATP7B trafficking from the Golgi network to the bile canaliculus membrane was observed in WIF-B9 cells, showing a need for Cu detoxification. This shows an increase in the intracellular Cu concentration, probably due to Cu release from endosomal CuO-NP solubilisation. Our data show that CuO-NP enter hepatic cells, most probably by endocytosis, bypassing the cellular defence mechanism against Cu, thus acting as a Trojan horse. Altogether, this study suggests that sub-toxic CuO-NP treatments induce successively a Cu overload, a Cu–Zn exchange on metallothioneins and MTF1 regulation on both Cu and Zn homeostasis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...