A metabolomic and pharmacokinetic study on the mechanism underlying the lipid-lowering effect of orally administered berberine†
Abstract
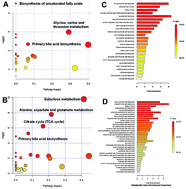
Clinical and animal studies demonstrated that orally administered berberine had a distinct lipid-lowering effect. However, pharmacokinetic studies showed that berberine was poorly absorbed into the body so the levels of berberine in the blood and target tissues were far below the effective concentrations revealed. To probe the underlying mechanism, the effect of berberine on the biological system was studied on a high-fat-diet-induced hamster hyperlipidemia model. Our results showed that intragastrically-administered berberine was poorly absorbed into circulation and most berberine accumulated in gut content. Although the bioavailability of intragastrically administered berberine was much lower than that of intraperitoneally administered berberine, it had a stronger lipid-lowing effect, indicating that the gastrointestinal tract is a potential target for the hypolipidemic effect of berberine. A metabolomic study on both serum and gut content showed that orally administered berberine significantly regulated molecules involved in lipid metabolism, and increased the generation of bile acids in the hyperlipidemic model. DNA analysis revealed that the orally administered berberine modulated the gut microbiota, and berberine showed a significant inhibition of the 7α-dehydroxylation conversion of cholic acid to deoxycholic acid, indicating a decreased elimination of bile acids in the gut. However, in model hamsters, elevated bile acids failed to downregulate the expression and function of CYP7A1 in a negative feedback loop. It was suggested that the hypocholesterolemic effect of orally administered berberine involves modulating the turnover of bile acids and the farnesoid X receptor signal pathway.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...