Hydrogel-enabled osmotic pumping for microfluidics: towards wearable human-device interfaces†
Abstract
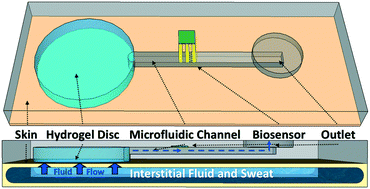
This paper describes a technique that utilizes the osmotic properties of hydrogels to passively draw fluid through a membrane and pass it along to a microfluidic network for sensing purposes. This technique may enable non-invasive collection and manipulation of sweat for biosensing. To demonstrate the concept, thin hydrogel discs equilibrated in saline or glycerol were integrated with a microfluidic device. The hydrogel interfaces with a water-permeable membrane. The high concentration of solute in the hydrogel creates an osmotic pressure difference across the membrane, driving fluid flow through the membrane and into the device. The release of solute from the hydrogel autonomously pumps the fluid into an adjacent microfluidic channel. The flowrate of liquid drawn through the membrane is controlled by the osmotic pressure of the hydrogel and its interfacial contact area with the membrane. The flowrate gradually decreases over time as the continuous influx of withdrawn fluid dilutes the concentrated solute in the hydrogel. Initial testing has shown the device can pump accurate levels of glucose across the membrane and through a microchannel to a reservoir with a glucose sensor. Sensors and electrodes can be implemented in future microfluidic devices operating on these principles to test for other bioanalytes in sweat.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...