A one-pot biosynthesis of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/bacterial cellulose (BC) nanocomposites†
Abstract
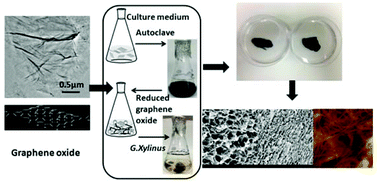
Here, we report for the first time a one-pot in situ biosynthetic method to fabricate structurally controllable bacterial cellulose (BC)/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) composites. Graphene oxide (GO) was highly reduced during a standard autoclave process using a traditional mannitol culture medium as the reducing agent. The RGO sheets prepared exhibit a high carbon to oxygen ratio of 3.1, as compared to 1.8 for GO determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The electrical conductivity of the RGO was found to be 23.75 S m−1. The final BC/RGO composites were developed in three distinct forms: sealed structures in water, aerogels characterized by a porous cross-section and an aligned longitudinal structure, and films embedded within the RGO sheets. Because of the simplicity and non-toxic nature of this work, this process can be used in biomedical and bioelectronics applications, which can be placed within the context of novel biocompatible materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...