1-Hexene: a renewable C6 platform for full-performance jet and diesel fuels†
Abstract
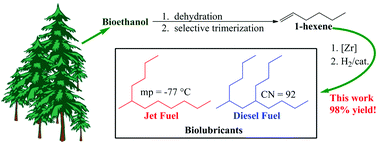
A highly efficient and selective process has been developed for the conversion of 1-hexene to jet and diesel fuels. In combination with commercial processes for the dehydration of ethanol and trimerization of ethylene, this work provides a basis for the synthesis of full-performance hydrocarbon fuels from bio-ethanol. Selective oligomerization of 1-hexene with a Cp2ZrCl2/MAO catalyst at ambient temperature and pressure resulted in 100% conversion of 1-hexene with >80% selectivity to a mixture of the dimer and trimer. The hydrogenated dimer had a −20 °C viscosity of only 3.5 mPa s, an exceptionally low freezing point of −77 °C, and a cetane number of 67 suggesting that it has performance characteristics suitable for both jet and diesel fuels. The hydrogenated trimer had a flash point of 128 °C, a cetane number of 92, a 40 °C viscosity of 3.1 mPa s, and a −20 °C viscosity of 24.5 mPa s. These properties suggest that the trimer has applications as a high-performance diesel fuel. In addition to the fuel-range hydrocarbons, heavier oligomers have potential as biolubricants which improves the carbon yield of useful products to near quantitative levels.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Conversion of biomass with heterogeneous catalysts

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...