Ag incorporated Mn3O4/AC nanocomposite based supercapacitor devices with high energy density and power density†
Abstract
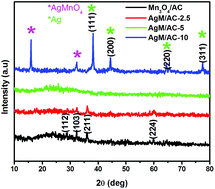
Silver incorporated Mn3O4/amorphous carbon (AC) nanocomposites are synthesized by a green chemistry method. X-ray diffraction studies revealed the structural changes in Mn3O4/AC nanocomposites attributable to the addition of silver. Cyclic voltammetry, charge–discharge and ac-impedance studies indicated that the Ag-Mn3O4/AC-5 electrode was the most suitable candidate for supercapacitor applications. From the galvanostatic charge–discharge studies, a higher specific capacitance of 981 F g−1 at a specific current of 1 A g−1 was obtained. An Ag-Mn3O4/AC-symmetric supercapacitor consisting of an Ag-incorporated Mn3O4/AC composite as an anode as well as a cathode, and an asymmetric supercapacitor consisting of an Ag-incorporated Mn3O4/AC composite as a cathode and an activated carbon as an anode have been fabricated. The symmetric device exhibits a specific cell capacitance of 72 F g−1 at a specific current of 1 A g−1 whereas the asymmetric device delivers a specific cell capacitance of 180 F g−1 at a high current rate of 10 A g−1. The asymmetric supercapacitor device yields a high energy density of 81 W h kg−1. This is higher than that of lead acid batteries and comparable with that of nickel hydride batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...