Urea-derived graphitic carbon nitride as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for CO2 conversion into cyclic carbonates†
Abstract
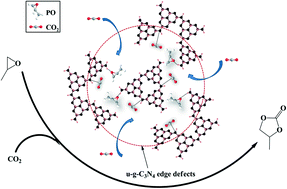
In order to overcome existing solid catalysts' disadvantages of low stability and activity, urea-derived graphitic carbon nitrides (u-g-C3N4) with higher stabilities and more active centers were prepared under different temperatures (550–450 °C). With a decrease in preparation temperature from 550 °C to 480 °C, a u-g-C3N4 of lower crystallinity with a smaller polymerization degree was obtained and found to have a higher catalytic activity for CO2 conversion into propylene carbonate. The higher activity of the u-g-C3N4 caused by decreasing the temperature might be ascribed to the lower crystallinity and polymerization degree, which led to more edge defects, wherein the incompletely-coordinated nitrogen atoms served as the main active sites in the cycloaddition reaction. Among all the prepared catalysts, that prepared at 480 °C (u-g-C3N4-480) showed the highest catalytic activity for CO2 conversion and exhibited great suitability for other epoxide substrates.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Carbon dioxide conversion

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...