Development of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors for neurodegeneration and neuropathic pain
Abstract
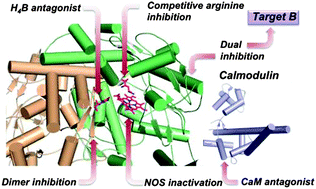
Nitric oxide (NO) is an important signaling molecule in the human body, playing a crucial role in cell and neuronal communication, regulation of blood pressure, and in immune activation. However, overproduction of NO by the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) is one of the fundamental causes underlying neurodegenerative disorders and neuropathic pain. Therefore, developing small molecules for selective inhibition of nNOS over related isoforms (eNOS and iNOS) is therapeutically desirable. The aims of this review focus on the regulation and dysregulation of NO signaling, the role of NO in neurodegeneration and pain, the structure and mechanism of nNOS, and the use of this information to design selective inhibitors of this enzyme. Structure-based drug design, the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of these inhibitors, and extensive target validation through animal studies are addressed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular Medicine and Neurodegenerative Diseases

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...