O2 adsorption dependent photoluminescence emission from metal oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
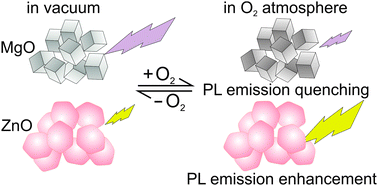
Optical properties of metal oxide nanoparticles are subject to synthesis related defects and impurities. Using photoluminescence spectroscopy and UV diffuse reflectance in conjunction with Auger electron spectroscopic surface analysis we investigated the effect of surface composition and oxygen adsorption on the photoluminescence properties of vapor phase grown ZnO and MgO nanoparticles. On hydroxylated MgO nanoparticles as a reference system, intense photoluminescence features exclusively originate from surface excitons, the radiative deactivation of which results in collisional quenching in an O2 atmosphere. Conversely, on as-prepared ZnO nanoparticles a broad yellow emission feature centered at hνEm = 2.1 eV exhibits an O2 induced intensity increase. Attributed to oxygen interstitials as recombination centers this enhancement effect originates from adsorbate-induced band bending, which is pertinent to the photoluminescence active region of the nanoparticles. Annealing induced trends in the optical properties of the two prototypical metal oxide nanoparticle systems, ZnO and MgO, are explained by changes in the surface composition and underline that particle surface and interface changes that result from handling and processing of nanoparticles critically affect luminescence.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bunsentagung 2014: ‘Physical Chemistry of Nanoparticles’

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...