Computational investigation of structural and electronic properties of aqueous interfaces of GaN, ZnO, and a GaN/ZnO alloy†
Abstract
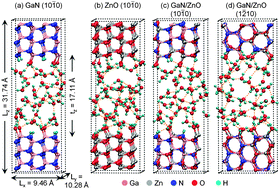
The GaN/ZnO alloy functions as a visible-light photocatalyst for splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen. As a first step toward understanding the mechanism and energetics of water-splitting reactions, we investigate the microscopic structure of the aqueous interfaces of the GaN/ZnO alloy and compare them with the aqueous interfaces of pure GaN and ZnO. Specifically, we have studied the (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface of GaN and ZnO and the (10
0) surface of GaN and ZnO and the (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) and (1
0) and (1![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 10) surfaces of the 1 : 1 GaN/ZnO alloy. The calculations are carried out using first-principles density functional theory based molecular dynamics (DFT-MD). The structure of water within a 3 Å distance from the semiconductor surface is significantly altered by the acid/base chemistry of the aqueous interface. Water adsorption on all surfaces is substantially dissociative such that the surface anions (N or O) act as bases accepting protons from dissociated water molecules while the corresponding hydroxide ions bond with surface cations (Ga or Zn). Additionally, the hard-wall interface presented by the semiconductor imparts ripples in the density of water. Beyond a 3 Å distance from the semiconductor surface, water exhibits a bulk-like hydrogen bond network and oxygen–oxygen radial distribution function. Taken together, these characteristics represent the resting (or “dark”) state of the catalytic interface. The electronic structure analysis of the aqueous GaN/ZnO interface suggests that the photogenerated holes may get trapped on interface species other than the adsorbed OH− ions. This suggests additional dynamical steps in the water oxidation process.
10) surfaces of the 1 : 1 GaN/ZnO alloy. The calculations are carried out using first-principles density functional theory based molecular dynamics (DFT-MD). The structure of water within a 3 Å distance from the semiconductor surface is significantly altered by the acid/base chemistry of the aqueous interface. Water adsorption on all surfaces is substantially dissociative such that the surface anions (N or O) act as bases accepting protons from dissociated water molecules while the corresponding hydroxide ions bond with surface cations (Ga or Zn). Additionally, the hard-wall interface presented by the semiconductor imparts ripples in the density of water. Beyond a 3 Å distance from the semiconductor surface, water exhibits a bulk-like hydrogen bond network and oxygen–oxygen radial distribution function. Taken together, these characteristics represent the resting (or “dark”) state of the catalytic interface. The electronic structure analysis of the aqueous GaN/ZnO interface suggests that the photogenerated holes may get trapped on interface species other than the adsorbed OH− ions. This suggests additional dynamical steps in the water oxidation process.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Photosynthesis: From Natural to Artificial

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...