Fluorescent carbon nanomaterials: “quantum dots” or nanoclusters?†
Abstract
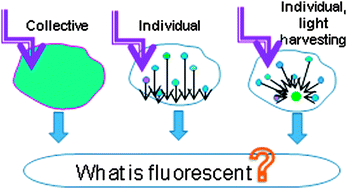
Despite many efforts, the mechanisms of light absorption and emission of small fluorescent carbon nanoparticles (C-dots) are still unresolved and are a subject of active discussion. In this work we address the question as to whether the fluorescence is a collective property of these nanoparticles or they are composed of assembled individual emitters. Selecting three types of C-dots with “violet”, “blue” and “green” emissions and performing a detailed study of fluorescence intensity, lifetime and time-resolved anisotropy as a function of excitation and emission wavelengths together with the effect of viscogen and dynamic fluorescence quencher, we demonstrate that the C-dots represent assemblies of surface-exposed fluorophores. They behave as individual emitters, display electronic anisotropy, do not exchange their excited-state energies via homo-FRET and possibly display sub-nanosecond intra-particle mobility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...