Self-assembly of discrete and polymeric metallosupramolecular architectures from cyclen-derived ligands†
Abstract
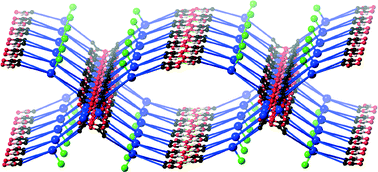
Two divergent ligands 1,4,7,10-tetrakis-(4-cyanobenzyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane L1 and 1,4,7,10-tetrakis-(4-carboxybenzyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane dihydrochloride dihydrate H6L2·2Cl·2H2O have been prepared and structurally characterised, and the solid-state structures of four new metal complexes have been elucidated. Ligand L1 was found to form a dimeric complex of the form [Ag2(L1)2]·2ClO4 when reacted with silver perchlorate, in which a macrocycle-bound Ag(I) ion is coordinated by the nitrile group of an adjacent ligand, forming a tightly-bound pair of Ag(I) ions supported by intramolecular π–π interactions. Compound H6L2·2Cl·2H2O was prepared by a solvothermal recrystallization following hydrolysis of the ester precursor, and forms a densely packed three-dimensional structure containing numerous hydrogen bonding interactions. Complexes [Ni(H4L2)Cl]2·[NiCl4]·2EtOH 2 and [Co(H4L2)Cl]2·[CoCl4]·2EtOH 3 were characterised as isostructural discrete macrocycle-bound Ni(II) and Co(II) species where the formation of rare hydrogen-bonded carboxylic acid tetramers gives rise to a series of 2-dimensional sheets, containing checkerboard-type cavities encapsulating alternating tetrachloridometallate anions and regions containing disordered solvent molecules. Complex poly-{[Cu2Cl(H2L1)(HOEt)]2·[CuCl4]·5H2O} 4 consists of a series of two-dimensional sheets formed from a macrocycle-bound CuCl species linked by copper paddlewheel clusters and hydrogen-bonded carboxylic acid dimers. Charge balance is again achieved by tetrachloridometallate anions, and the sheets undergo parallel 2D → 2D interpenetration. The influence of the flexible geometry and donor ability of the methylene-linked pendant arms is clearly visible when comparing discrete complex 1 with hydrogen-bonded networks 2 and 3 and polymeric species 4. The presence of tetrachloridometallate counterions resulting from the presence of excess chloride ions in the reaction mixtures also provides powerful structure-directing effects in complexes 2, 3 and 4.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Structural Macrocyclic Supramolecular Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...