Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for protein partitioning†
Abstract
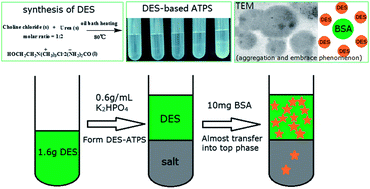
Four kinds of green deep eutectic solvent (DES) were synthesized, including choline chloride (ChCl)–urea, tetramethylammonium chloride (TMACl)–urea, tetrapropylammonium bromide (TPMBr)–urea and ChCl–methylurea. An aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) based ChCl–urea DES was studied for the first time for the extraction of bovine serum albumin (BSA). Single factor experiments proved that the extraction efficiency of BSA was influenced by the mass of the DES, concentration of K2HPO4 solution, separation time and extraction temperature. The optimum conditions were determined through an orthogonal experiment with the four factors described above. The results showed that under the optimum conditions, the average extraction efficiency could reach up to 99.94%, 99.72%, 100.05% and 100.05% (each measured three times). The relative standard deviations (RSD) of extraction efficiencies in precision, repeatability and stability experiments were 0.5533% (n = 5), 0.8306% (n = 5) and 0.9829% (n = 5), respectively. UV-vis and FT-IR spectra confirmed that there were no chemical interactions between BSA and the DES in the extraction process, and the CD spectra proved that the conformation of BSA did not change after extraction. The conductivity, DLS and TEM were combined to investigate the microstructure of the top phase and the possible mechanism for the extraction. The results showed that hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding interactions and the salting-out effect played important roles in the transfer process, and the aggregation and surrounding phenomenon were the main driving forces for the separation. All of these results proved that ionic liquid (IL)-based ATPSs could potentially be substituted with DES-based ATPSs to offer new possibilities in the extraction of proteins.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...