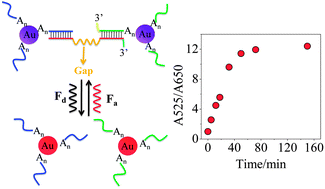
Due to great potential in nanobiotechnology, nanomachines, and smart materials, DNA-directed disassembly of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) has been extensively explored. In a typical system, nonbase-paired regions (e.g., overhangs and gaps in the linker DNA and oligonucleotide spacers between thiol group and hybridization sequence) are indispensable portions in the disassembly of AuNPs based on DNA displacement reaction. Therefore, it is necessary to study the effect of nonbase-paired regions to improve the kinetics of disassembly of AuNPs. Herein, the disassembly rate of AuNPs based on DNA displacement reaction was investigated by using different length spacers and linker DNA containing various lengths of gaps or overhangs. Interestingly, it was revealed that among the gaps in the linker DNA could be most effectively used to improve the disassembly rate of the AuNPs. As a result, when we introduced gaps into linker DNA, the DNA displacement reaction of AuNPs was markedly shortened to less than 50 min, which was much faster than the previous methods. As a proof of the importance of our findings, a rapid AuNP-based colorimetric DNA biosensor has been successfully prepared. In addition, we showed that the signal of the biosensors could be further amplified using exonuclease III, resulting in a much lower detection limit in comparison with previous sensors similarly using AuNP aggregates as probes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...