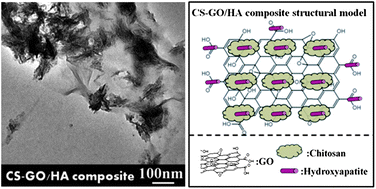
Motivated by the success of using graphene oxide (GO) as a nanofiller of composites, there is a drive to search for this new kind of carbon material as a reinforcing phase in biocomposites. In the present work, graphene oxide and chitosan (CS) functionalized graphene oxide were introduced as templates to fabricate hydroxyapatite (HA) using a facile solution-based in situ synthesis method, and GO–HA and CS-GO–HA nanocomposites were successfully prepared for the first time. It was found that the spindle like HA nanoparticles with a diameter of about 27 ± 7 nm and a length around 150 ± 25 nm were decorated randomly and strongly on the surface or aggregated at the edges of the pristine and chitosan functionalized GO matrix. Compared with HA, the prepared GO-based HA nanocomposites displayed an increased elastic modulus and hardness. The in vitro cytotoxicity of the prepared nanocomposites was investigated using CCK-8 assay on murine fibroblast L-929 cell line and human osteoblast-like MG-63 cell line, respectively. Both of the nanocomposites exhibited a high cell proliferation rate for L-929 and MG-63, and the CS-GO–HA could provide significantly higher cell viability and alkaline phosphatase activity compared to the GO–HA composite. These findings may provide new prospects for utilizing the GO-based hydroxyapatite biocomposites in bone repair, bone augmentation, as well as coating of biomedical implants and broaden the application of GO sheets in biological areas.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...