Modification of TiO2 by bimetallic Au–Cu nanoparticles for wastewater treatment†
Abstract
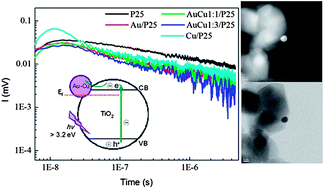
Au, Cu and bimetallic Au–Cu
* Corresponding authors
a Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, People's Republic of China
b
Laboratoire de Chimie Physique, CNRS-Université Paris-Sud, UMR 8000 CNRS, Bât. 349, 91405 Orsay, France
E-mail:
hynd.remita@u-psud.fr
Fax: +33 (0)1 69 15 30 55
Tel: +33 (0)1 69 15 72 58
c Department of Physics & Astronomy, The University of Texas at San Antonio, One UTSA Circle, San Antonio, TX 78249, USA
d Laboratoire de Réactivité de Surface, UPMC Université Paris 6, UMR 7197-CNRS, 3 rue Galilée, 94200 Ivry, France
e Institut Lavoisier de Versailles, CNRS UMR 8180, 45 Avenue des Etats Unis, 78035 Versailles, France
Au, Cu and bimetallic Au–Cu

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Z. Hai, N. El Kolli, D. B. Uribe, P. Beaunier, M. José-Yacaman, J. Vigneron, A. Etcheberry, S. Sorgues, C. Colbeau-Justin, J. Chen and H. Remita, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 10829 DOI: 10.1039/C3TA11684K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
