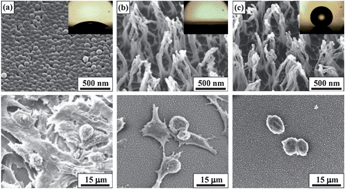
The control of cancer cell adhesion behavior on certain surfaces has been widely studied in recent years to enhance cell adhesion, which is required for bio-sensing, implant biomaterials, or to prevent infections from bacteria or germs. In addition, it helps to preserve the original functions of medical devices such as implants, catheters, injection syringes, and vascular stents. In this study, we explored the behavior of mouse liver cancer cells on nanostructured surfaces in extreme wetting conditions of a superhydrophobic or superhydrophilic nature. Oxygen plasma treatment of polymeric surfaces induced the formation of nanostructures such as bumps or hairs with various aspect ratios, which is defined as the height to diameter ratio. A superhydrophobic surface with a contact angle (CA) of 161.1° was obtained through the hydrophobic coating of a nanostructured surface with a high aspect ratio of 25.8. On the other hand, an opposite extreme wetting surface with a superhydrophilic nature with a CA of 1.7° was obtained through the hydrophilic coating of the same structured surface. The mouse liver cancer cells significantly proliferated on a mild hydrophilic surface with a low aspect ratio nanostructure due to the mild roughness and improvements of mechanical anchoring. However, the superhydrophilic surface with a high aspect ratio nanostructure (i.e., hair shaped) suppressed the growth of the cancer cells due to the limited number of sites for focal adhesion, which restricted the adhesion of cancer cells and resulted in a decrease in the cell-covered area. The superhydrophobic nanostructured surface with a high aspect ratio further restricted the adhesion and growth of the cancer cells; the cell activity was extremely suppressed and the spherical shape of the cancer cells was maintained. Thus, this simple method for fabricating nanostructured surfaces with various wetting conditions might be useful for producing biomedical devices such as stents, implants, drug delivery devices, and detection and/or sensing devices for cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...