BMP2-loaded nanoporous silica nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells†
Abstract
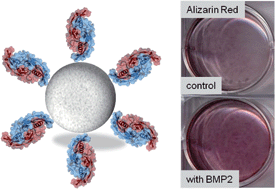
Nanoporous (or mesoporous) silica materials have been extensively investigated as a novel biomaterial in the last few years, especially with regard to bone tissue engineering. Due to their high specific surface areas, capability for chemical modification, and their large pore volumes, nanoporous silica nanoparticles (NPSNPs) are of tremendous interest as drug delivery systems. In this study, we describe the immobilization of the bone growth factor BMP2 on NPSNPs in biologically relevant amounts, using coupling via an aminosilane linker. The amount of BMP2 loaded onto NPSNPs was determined using two different methods. The biocompatibility of NPSNPs was tested with different cell lines upon exposure to different particle concentrations. Whereas standard cell types (HepG2, NIH3T3) are relatively insensitive against NPSNPs, adMSC cells (adipose-derived human mesenchymal stem cells) show a somewhat reduced viability. adMSC cells were also used to test for the osteoinductive effect of the BMP2-carrying NPSNPs. Histological staining reveals the osteogenic differentiation of the human mesenchymal stem cells. Even BMP-free amino-modified NPSNPs show a certain osteoinductive effect, which is however significantly stronger with immobilized BMP2 and can furthermore be enhanced by supplemental dexamethasone. We therefore suggest that NPSNPs carrying BMP2 are suitable for application in bone tissue engineering, e.g. in the construction of scaffolds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioactive surfaces for hard tissue regeneration

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...