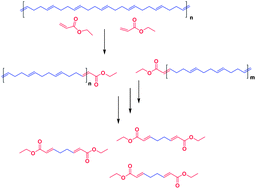
We have successfully depolymerized polybutadiene via an insertion metathesis mechanism. This new concept involves the irreversible depolymerization of unsaturated polymers with electron deficient olefins. The product of the degradation was characterized by NMR and GC-MS. We also explored the use of copper iodide as an additive. We observed significant reduction of molecular weight under a variety of conditions with the most extensive depolymerization occurring with the use of Grubbs 2nd generation catalyst with CuI. Finally, polybutadiene was converted to a polyamide by performing insertion metathesis depolymerization with acryloyl chloride and subsequently reacting with 1,6-diaminohexane, demonstrating the potential of polymer-to-polymer conversions with this chemistry.