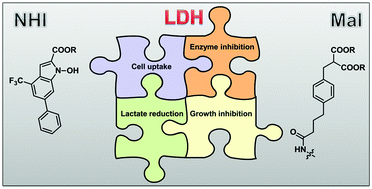
A head-to-head study of representative examples of N-hydroxyindole-2-carboxylates (NHI) and malonic derivatives (Mal) as LDH-A inhibitors was conducted, comparing the enzyme inhibition potency, cellular uptake, reduction of lactate production in cancer cells and anti-proliferative activity. Among the compounds tested, methyl 1-hydroxy-6-phenyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxylate (2, NHI-2), a methyl ester belonging to the NHI class, displayed optimal properties in the cell-based assays, proving to be an efficient anti-glycolytic agent against cancer cells.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...