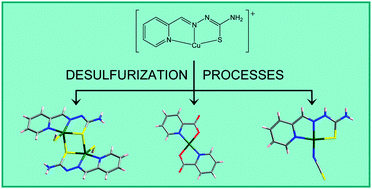
This work provides structural evidence for different desulfurization processes in aqueous solutions of [CuL]+ derivatives (HL = pyridine-2-carbaldehyde thiosemicarbazone). Structural resolution has been achieved for the [{CuL(SH)}2] (1), [CuLCl]2[Cu(pic)2] (pic− = picolinato, pyridine-2-carboxilato) (2) and [Cu(HL)(NCS)](NO3) (4) compounds, together with a derivative of 4 with formula [Cu(HL)(NCS)][Cu(HL)(NCS)0.72(NO3)0.28](NO3)2 (5), whose HS−, pic− and NCS− ligands come from thiosemicarbazone breakage. The behaviour of the [CuL]+ species in basic aqueous solutions or water under reflux has been compared with that exhibited by iron(III), cobalt(III), zinc(II) and lead(II) derivatives of the same thiosemicarbazone ligand. [Cu(L′)]+ species (HL′ = pyridine-2-carbaldehyde N4-methylthiosemicarbazone) have also been analyzed by infrared spectroscopy or mass spectrometry under the same experimental conditions. In addition, preparative methods for a rational synthesis of the serendipitously obtained compounds are proposed. In this way, the crystal structure of [CuL(pic)]·3H2O (3) has been elucidated too. The partial desulfurization of coordinated thiosemicarbazones could lead to a reinterpretation of their biological activity with consequences for the search for possible therapeutic uses.