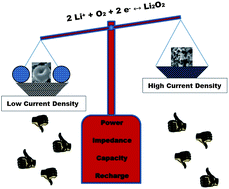
We report a significant difference in the growth mechanism of Li2O2 in Li–O2 batteries for toroidal and thin-film morphologies which is dependent on the current rate that governs the electrochemical pathway. Evidence from diffraction, electrochemical, FESEM and STEM measurements shows that slower current densities favor aggregation of lithium peroxide nanocrystallites nucleated via solution dismutase on the surface of the electrode; whereas fast rates deposit quasi-amorphous thin films. The latter provide a lower overpotential on charge due to their nature and close contact with the conductive electrode surface, albeit at the expense of lower discharge capacity.