Urchin-like NixPy hollow superstructures: mild solvothermal synthesis and enhanced catalytic performance for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol
Abstract
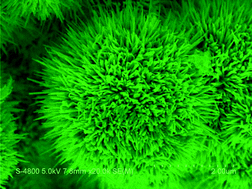
In this paper, a two-step solution process was designed for the preparation of urchin-like NixPy hollow superstructures with enhanced catalytic performance for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Firstly, nickel microspheres were solvothermally fabricated through the reaction between N2H4·H2O and NiCl2·6H2O in glycol at 170 °C for 2 h. Then, urchin-like NixPy hollow superstructures were obtained at 160 °C for 6 h via an ethanol–water mixed solvothermal route, employing freshly-prepared Ni microspheres and white phosphorus as the reactants. The as-obtained superstructures were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS). The time-dependent shape evolution experiments confirmed that the formation of urchin-like NixPy hollow superstructures was attributed to the Kirkendall effect. Experiments discovered that Ni microspheres, Ni@NixPy core–shell structures and urchin-like NixPy hollow superstructures could be used as catalysts for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. The order of their catalytic activities was Ni microspheres < Ni@NixPy core–shell structures < urchin-like NixPy hollow superstructures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...