Application of Co(ii) complex multi-wall carbon nanotube modified carbon paste electrodes for electrocatalytic determination of hydroxylamine†
Abstract
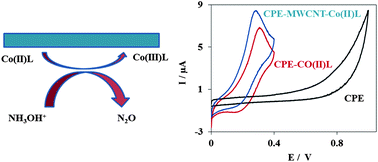
The electrocatalytic oxidation of hydroxylamine was studied on a cobalt(II) bis(benzoylacetone) ethylenediimino multi-wall carbon nanotube modified carbon paste electrode (Co(II)L-MWCNT-CPE). The prepared electrode shows very efficient electrocatalytic activity for the oxidation of hydroxylamine via substantially decreasing the anodic overpotential and increasing the anodic current. The electron transfer coefficient (α) between hydroxylamine and the modified electrode surface was determined from the rising part of the current–voltage curve of the cyclic voltammogram (CV) and was found to be 0.54. The catalytic current presents linear dependence for concentrations of hydroxylamine from 5.0–50.0 μM with a detection limit of 1.2 μM by square wave voltammetry. The relative standard deviation (% RSD) for 10 replicate measurements of 20.0 μM hydroxylamine was ±3.7%. The independency of this method from the presence of interferences was studied. Finally the method was applied to the determination of hydroxylamine in water and pharmaceutical samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...