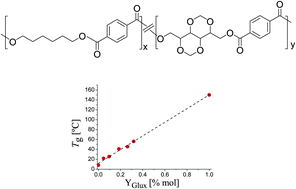
The diacetalized diol 2,4:3,5-di-O-methylene-D-glucitol (Glux), a bicyclic compound derived from D-glucose, was used as a comonomer of 1,6-hexanediol in polycondensation in the melt with dimethyl terephthalate to produce a set of aromatic copolyesters (PHxGluxyT) with Glux contents ranging from 5 to 32%-mole. These sustainable copolyesters had molecular weights within the 12,000 to 45,000 g mol−1 range, and polydispersities between 2.0 and 2.5. They all had a random microstructure and displayed slight optical activity. PHxGluxyT showed a good thermal stability and were semicrystalline with both crystallinity degree and crystallization rate decreasing as the content in Glux increased. Conversely, Tg increased with the incorporation of Glux going from 8 °C in PHT to near 60 °C in the copolyester containing 32%-mole Glux. Compared to PHT, PHxGluxyT copolyesters showed not only an enhanced susceptibility to hydrolysis but also an appreciable biodegradability in the presence of lipases.