Controlled grafting of cellulose fibres – an outlook beyond paper and cardboard†
Abstract
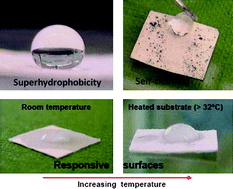
Cellulose is highly interesting from a materials science perspective, very much fuelled by its abundance, renewability and low cost. In this review, the heterogeneous grafting of cellulose fibres through controlled
- This article is part of the themed collection: New methods of polymer synthesis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...