Abstract
Covering: up to February 2012
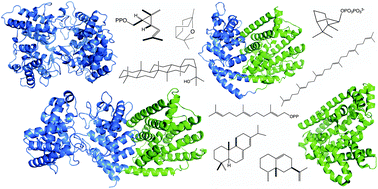
The complexity of terpenoid natural products has drawn significant interest, particularly since their common (poly)isoprenyl origins were discovered. Notably, much of this complexity is derived from the highly variable cyclized and/or rearranged nature of the observed hydrocarbon skeletal structures. Indeed, at least in some cases it is difficult to immediately recognize their derivation from poly-isoprenyl precursors. Nevertheless, these diverse structures are formed by sequential elongation to acyclic precursors, most often with subsequent cyclization and/or rearrangement. Strikingly, the reactions used to assemble and diversify terpenoid backbones share a common carbocationic driven mechanism, although the means by which the initial carbocation is generated does vary. High-resolution crystal structures have been obtained for at least representative examples from each of the various types of enzymes involved in producing terpenoid hydrocarbon backbones. However, while this has certainly led to some insights into the enzymatic structure–function relationships underlying the elongation and simpler cyclization reactions, our understanding of the more complex cyclization and/or rearrangement reactions remains limited. Accordingly, selected examples are discussed here to demonstrate our current understanding, its limits, and potential ways forward.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Structural Aspects of Biosynthesis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...