Photocrosslinkable dextran hydrogel films as substrates for osteoblast and endothelial cell growth†
Abstract
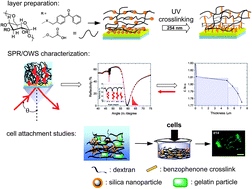
Functional hydrogel films on solid supports are versatile materials with large potential for cell growth and tissue engineering. Here, we report on a modular approach to generate functional hydrogel composite films for endothelial and osteoblast cell co-culture. The
- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials for biosurfaces

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...