Enzymatic synthesis of amoxicillin by penicillin G acylase in the presence of ionic liquids
Abstract
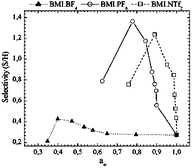
A major obstacle for the industrial implementation of the enzymatic synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics is the limited yield of the product, due to undesirable hydrolytic reactions. This drawback can be partially avoided by reducing the water activity in the medium. Ionic liquids (ILs) have emerged as an alternative to conventional organic media due to their high thermal and chemical stability, negligible vapor pressure, non-flammability, and easy recycling. In this context, this paper assesses the catalytic activity of penicillin G acylase (E.C.3.5.1.11) in the synthesis of amoxicillin using different ILs, all based on the 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium cation. An increase of 400% in selectivity (synthesis/hydrolysis, S/H ratio) was observed for the reactions carried out with BMI·PF6 as a cosolvent at 75% (vIL/vwater) when compared to the totally aqueous medium (using phosphate buffer). This figure reached 350% for BMI·NTf2, while for BMI·BF4 there was only a slight increase in selectivity. The highest conversion of the β-lactam nucleus (6-APA) was achieved using BMI·NTf2 as a cosolvent at 71% (v/v), more than 36% above the one in water. No deactivation of the enzyme after the reactions was observed in any of the ILs, and the physical integrity of the biocatalyst particles was maintained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...