Design of environmentally friendly ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient and high activity extraction of proteins
Abstract
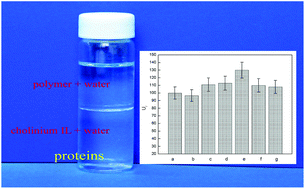
Ionic liquids (ILs) have numerous applications in industrial processes as a benign alternative to conventional volatile organic solvents. However, many of them are toxic to organisms and are poorly biodegradable. In this work, a series of environmentally friendly cholinium ILs have been designed and synthesized. It was found that these ILs could form aqueous two-phase systems (ATPSs) with polypropylene glycol 400 (PPG400) which is thermo-sensitive, non-toxic and biodegradable. In order to understand the phase formation processes and possible application of these ATPSs for extraction/separation of proteins, the binodal curves and tie lines of these ATPSs were measured at 25 °C, and the effects of anionic structure of the ionic liquids, nature of the proteins and difference in the concentration of top- and bottom-phases on the partitioning behavior of some typical proteins were investigated systematically. It was shown that bovine serum albumin (BSA), trypsin, papain and lysozyme could be enriched effectively into the ionic liquid-rich phase of the ATPSs, and single-step extraction efficiency could be as high as 86.4–99.9% under the optimized conditions. Furthermore, enzyme activity of the native trypsin in water and in aqueous ionic liquid solutions was determined by using N-a-benzoyl-L-arginine ethyl ester as a substrate, and activity increases to about 127% was observed after 13 months storage. In addition, PPG400 has been recovered simply by heating and reused in the next extraction processes. This avoids the non-sustainable issue of highly salty water produced in the application of the polyethylene glycol (PEG) + salt and ionic liquid + salt ATPSs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...