Reaction network governing diphosphine-protected gold nanocluster formation from nascent cationic platforms†
Abstract
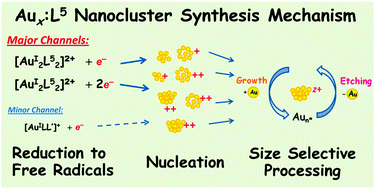
We identify the reaction network governing gold monolayer protected cluster (MPC) formation during the reduction of Au(PPh3)Cl and L5 (L5 =

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...