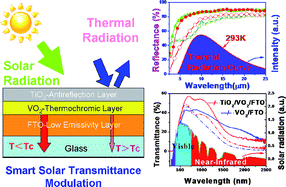
Vanadium dioxide is a key material for thermochromic smart windows that can respond to environmental temperatures to modulate near infrared irradiation from a transparent state at low-temperature to an opaque state at high-temperature while maintaining the visible transmittance. This paper reports a novel VO2/FTO/glass multi-layered structure, which shows promising optical properties for application to energy-efficient smart windows. VO2 thin films are deposited on F-doped SnO2 (FTO) glasses by annealing a precursor film that is obtained via a solution-based process. The rutile-structured FTO substrate enhances the crystallinity of the VO2 films and lowers the synthesis temperature to ∼390 °C. The VO2/FTO/substrate double-layered films show both improved low-emissivity performance and distinct thermochromic properties. For a 65 nm thick VO2/FTO substrate double-layered film, low emissivities of 0.19 and 0.27 before and after the metal-insulator phase transition (MIPT) are obtained, while a solar transmittance modulation efficiency (η, in the wavelength range of 280–2600 nm) of 4.9% is achieved. A TiO2 anti-reflective coating (ARC) is incorporated to form a three-layered TiO2/VO2/FTO/substrate structure to boost the integrated visible transmittance (Tvis) while maintaining the low-emissivity performance. A 29.4% improvement for Tvis from 34.0% to 44.0% at room temperature is achieved for a 55 nm thick VO2 film coated with a TiO2 layer while emissivities of 0.13 and 0.24 before and after MIPT are maintained. Moreover, η is also increased significantly, from 4.3% for the VO2/FTO/substrate structure to 8.8% for the TiO2/VO2/FTO/substrate structure. Our results demonstrate a new approach of combining both thermochromism and low-emissivity performance for applications such as VO2-based energy-saving windows.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...