Electrochemical behaviour and voltammetric sensitivity at arrays of nanoscale interfaces between immiscible liquids†
Abstract
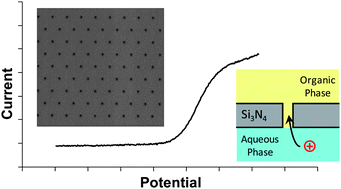
Arrays of nanoscale interfaces between immiscible electrolyte solutions were formed using
- This article is part of the themed collection: Future Electroanalytical Developments

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...