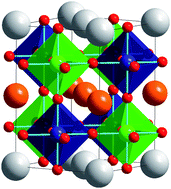
Although both A- and B-site cations have the same simple cubic topology in the perovskite structure they typically adopt different patterns of chemical order. As a general rule B-site cations order more readily than A-site cations. When cation ordering does occur, rock salt ordering of B/B′ cations is favored in A2BB′X6 perovskites, whereas layered ordering of A/A′ cations is favored in AA′B2X6 and AA′BB′X6 perovskites. The unexpected tendency for A-site cations to order into layers stems from the bond strains that would result at the anion site if A and A′ cations of different size were to order with a rock salt arrangement. The bonding instabilities that are created by layered ordering are generally offset either by anion vacancies or second order Jahn–Teller distortions of a B-site cation. Novel types of A-site cation ordering can be stabilized by a+a+a+ or a+a+c− tilting of the octahedra.