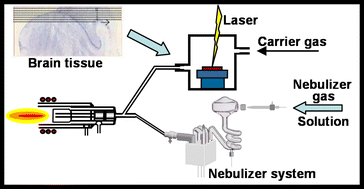
A novel solution-based calibration method for quantitative spatial resolved distribution analysis (imaging) of elements in thin biological tissue sections by LA-ICP-MS (laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry) is described. A dual flow of the carrier and nebulizer gas is used to transport the aerosol of the laser ablated solid sample (brain tissue) and that of the nebulized aqueous standard into inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source, respectively. Both aerosols are introduced separately in the injector tube inside a special ICP torch and then mixed in the inductively coupled plasma. Calibration curves were obtained via two different calibration strategies: (i) solution based calibration and (ii) with a set of well characterized homogeneous brain laboratory standards. In the first approach matrix matching is performed by solution nebulization of a series of aqueous standards with defined analyte concentrations and simultaneous laser ablation of brain homogenate followed by nebulization of 2% (v/v) HNO3 and laser ablation of a whole brain slice (line by line). In the second approach of calibration a set of brain homogenates with defined analyte concentrations is analyzed by LA-ICP-MS followed by the imaging of brain tissue under the same experimental conditions (dry plasma). Calibration curves of elements of interest (e.g., Li, Na, Al, K, Ca, Ti, V, Mn, Ni, Co, Cr, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Rb, Sr, Y, Cd, Ba, La, Ce, Nd, Gd, Hg, Pb, Bi and U) were obtained using (i) aqueous standards or (ii) the set of synthetic laboratory standards prepared from a mouse brain homogenate doped with elements at defined concentrations. The ratio of the slope of the calibration curves (obtained by using aqueous standards and solid standards) was applied to correct the differences of sensitivity among ICP-MS and LA-ICP-MS. Quantitative images of Li, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn and Rb in mouse brain were obtained under wet plasma condition (nebulization of HNO3 solution in parallel with ablation of solid brain sample).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...